Periodic table of elements
that the basic component of matter is an atom;
what is the atomic number;
what is the atomic mass;
what are the symbols and names of elements;
that the elements are divided into metals and non‑metals.
interpret periodic law;
describe the structure of the periodic table (indicate groups and periods);
determine the location of the element in the periodic table;
indicate metals and non‑metals in the periodic table;
check information about the element (atomic number, atomic mass, type of element) from the periodic table basic information about the element.
How were the elements classified?
The nineteenth century was the time when scientists already knew several dozens of chemical elements. These were examined and described by them. Scientists at the time noticed that among the elements there are those that exhibit similar properties. They were looking for a key according to which they could organize and classify them.
Using the Internet, a textbook and e‑textbook, find information on the history of classification of elements. Answer the questions:
Who - name scientists - made attempts to classify elements?
What common features did the scientists notice?
Who formulated the periodic law?
How is the periodic table of elements built?
Periodic table of elementsPeriodic table of elements is a table listing of all chemical elements ordered by increasing atomic number. The elements are grouped according to cyclically similar properties. Columns are called groups, and rows are called periods. Groups and periods are numbered.
All groups have been given names that come from the names of the elements at the beginning of the group. Elements belonging to the same group have similar properties. The exception is hydrogen. Although it is located in a group of alkali metals, because of its properties it does not belong to any of the groups.
Consider the minimum number of parameters that should be given to determine the location of the element in the periodic table? In how many ways can you describe the location of the element in this table?
What shapes can periodic table have?
Some scientists have developed periodic tables with different shapes. However, the method of presenting elements in the form of a table is the most commonly used. It has also been approved by The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, abbreviation IUPAC – organization dealing, inter alia, with the standardization of symbols, nomenclature and patterns used by chemists around the world.
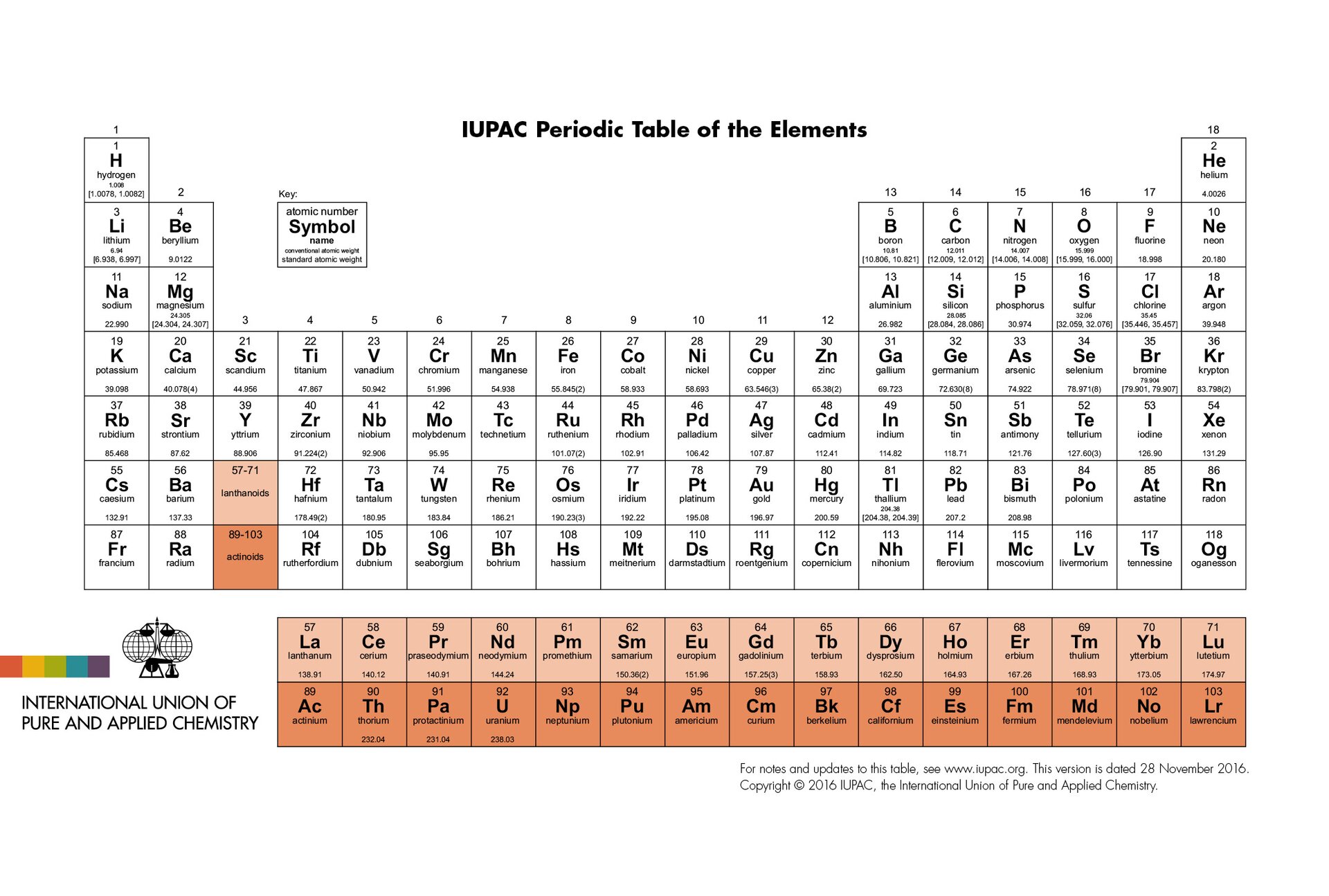
The simplest version of the periodic table contains numbered symbols of chemical elements, group numbers and periods. However, there are also such versions that present other additional information (e.g. names of elements and their properties, structure of their atoms, size of atoms, etc.). Regardless of how much information about elements are contained in periodic table, the order of elements, the number of groups, the type of elements in the group and period are identical in each periodic table of elements.

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
The periodic table consists of 7 rows called Periods, going across, and 18 columns, called Groups going down. The elements in the Periodic Table are arranged according to their atomic number, which is the number of protons in their nucleus. The Period shows the element’s electron shell that is being filled. For example sodium is in Period 3 and Group 1. So it has electronic configuration 2:8:1. Whereas chlorine which is also in Period 3 but Group 17 has electronic configuration 2:8:7. So in both cases it is the third shell that is being filled. The group an element is in gives the number of electrons in the outer shell of an atom of that element. Chemical reactions are to do with movement of electrons. So, as all elements in a particular group have the same number of outer shell electrons they have similar chemical reactions. There are trends in properties across Periods. As you look at the elements across the periodic table, from left to right across a period, the elements change from metals to non‑metals. There is also a decrease in atomic radius. This is because more protons in the nucleus pull the electrons in. Going from left to right there is an increase in the ionisation energy, that is the energy needed to remove the outermost electron. There is also an increase in electronegativity, which means the attraction of a bonded atom for the pair of electrons in a covalent bond. There are also trends in properties as you move down a Group. As you go down a group, the elements become more metallic. This is seen clearly in group 14 where carbon in period 2 is a non‑metal and lead in period 6 is a metal. Going down a group, there is also an increase in atomic radius, which means that an extra shell of electrons is added for each successive element. There are three groups that are usually studied: group 1 called the alkali metals, group 7 called the halogens, and group 18 called the noble gases. As we go down the group 1, the metals become more reactive as metals react by losing electrons and it is easier to lose the outer shell electron the further it is from the positive nucleus.As we go down the group 17, the non‑metals become less reactive as non‑metals react by gaining electrons and the fewer shells the greater attraction for the incoming electron. Group 18 elements have a full outer shell of electrons and so are very unreactive. Their densities and boiling points increase on going down the group.
Indicate which of the elements is more chemically active:
| sodium □ | potassium □ |
| potassium □ | calcium □ |
| chlorine □ | bromine □ |
| oxygen □ | fluorine □ |
Organize the symbols of elements by adding them to appropriate groups according to increasing atomic mass.
Fr, Be, Sr, Mg, Ge, C, Ca, Li, Ba, Sn, K, Pb, Si, Na
| ALKALI METALS: | |
|---|---|
| ALKALINE EARTH METALS: | |
| CARBON GROUP: |
Mark the division between metals and non-metals on the periodic table of elements (blue). Circle a group of noble gases (yellow) and 5 period (green). Compare your solution with other students.
Which answer is correct. Calcium:
- is located in the fourth period and the second group, has two electron shells and two valence electrons
- is located in the second period and the fourth group, has two electron shells and two valence electrons
- it is located in the fourth period and the second group, has four electron shells and two valence electrons
- it is located in the fourth period and the second group, has four electron shells and four valence electrons
Summary
Periodic table of elements is a universal way of presentation of chemical elements.
In the periodic table, the elements (their symbols) are placed sequentially in the table according to the growing atomic number.
Vertical columns are called groups and horizontal rows – periods. All groups and periods are numbered.
Elements belonging to one group have similar properties (except for hydrogen).
Find following elements in the periodic table:
element from the helium group used to fill some light bulbs;
element from the boron group used for making cans for beverages;
element from the second group of the periodic table, the main component of the bones.
Keywords
periodic table of elements, period, group, Mendeleev, chemical element
Glossary
układ okresowy pierwiastków – tablica przedstawiająca wszystkie pierwiastki chemiczne, uporządkowane kolejno według rosnącej liczby atomowej, w grupach (obejmujących pierwiastki o podobnych właściwościach) i okresach (w których właściwości pierwiastków zmieniają się stopniowo)