Prehistory
to explain how human evolution of human took place and where it started;
to describe how the theory of evolutiontheory of evolution was created and who its author is;
to characterize how the first people lived;
to tell about the first inventions and achievements of humankind;
to explain what the Neolithic revolutionNeolithic revolution was;
to define the significance of the Neolithic revolutionNeolithic revolution for the history of humankind;
to talk about the oldest human settlements and buildings.
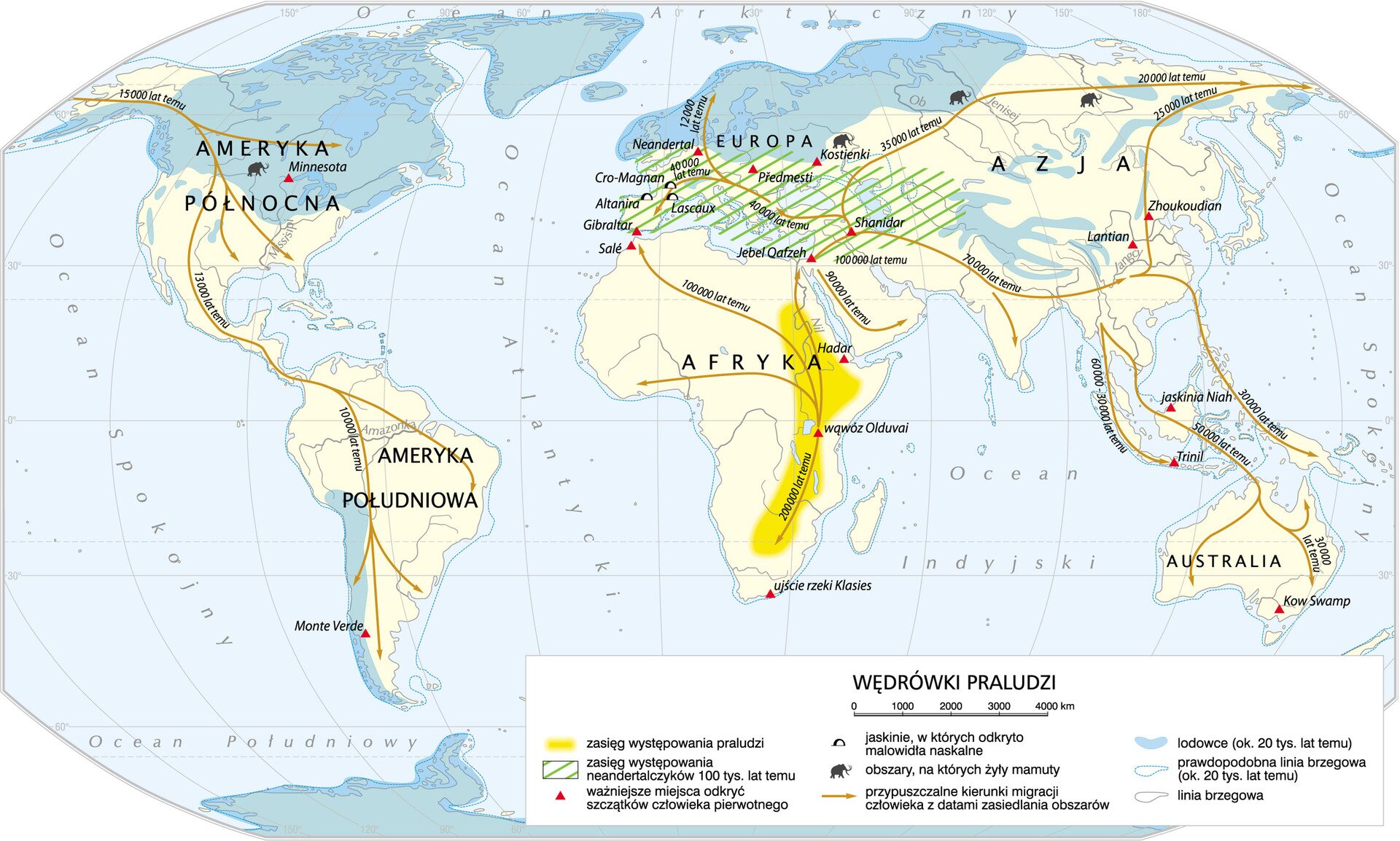
PrehistoryPrehistory is the longest period in history. Its duration as a period in the history of humankind is starts from the moment of appearance of hominidshominids (the Hominidae) in Africa about 2.5 million years ago, and ends with the invention of writing in the early 4th millennium B.C. During this period, a complicated process of human evolution took place, the last stage of which was the appearance of Homo sapiens sapiens, the human. The creator of the theory of evolutiontheory of evolution is considered to be the British naturalist Charles Darwin, who in his work On the Origin of Species described the transformations taking place in the world of animals adapting to environmental changes. The early humans led nomadic lives and lived in groups of enough numbers to take care of their safety and find food together. By means of trials and errors, they learned about the world around them and gained the necessary experience to survive. Over time, they learned to make a fire, hunt animals or build shelters. A great breakthrough in the history of humankind was the ability to produce and improve tools, such as hand axeshand axes, i.e. primitive knives fitted to the hands, and the art of lighting fire, thanks to which predators could be driven away and more nutritious food could be prepared. Primitive people have also left traces of art – which can be found in more than a hundred caves all over Spain and France. About 14 thousand years ago, the climate started to warm up after the Ice Age, known as PleistocenePleistocene. During the Ice Age, most of the large mammals died out, and there was a clear change – the large plains of the Northern Hemisphere, freed from ice, were covered by lush vegetation. Humans had to adapt to the changes taking place around them – they started to live a sedentary lifestyle, cultivate the land and breed animals. It took place about 8 thousand years B.C. in the area of the so‑called Fertile CrescentFertile Crescent, starting a ground‑breaking stage of the development in the history of humankind. Neolithic revolutionNeolithic revolution, which was the name given to these changes in history, caused the communities, which so far had been leading a hunter‑gatherer lifestyle, to settle in convenient and fertile areas, giving rise to the first urban centres. One of the first and best preserved NeolithicNeolithic settlements to this day is Catal Huyuk, in the territory of today's Turkey, the origins of which are estimated at about 8‑10 thousand years.
Look at the illustration and learn about the history of Charles Darwin, the creator of the theory of evolution.
alternative description 5. Charles Darwin always caught and ate at least one piece of each newly discovered species. And agouti's meat, a rodent related to the guinea pig, he even described as the best meat he ever ate.
Describe how the appearance of the early humans has changed over hundreds of thousands of years.
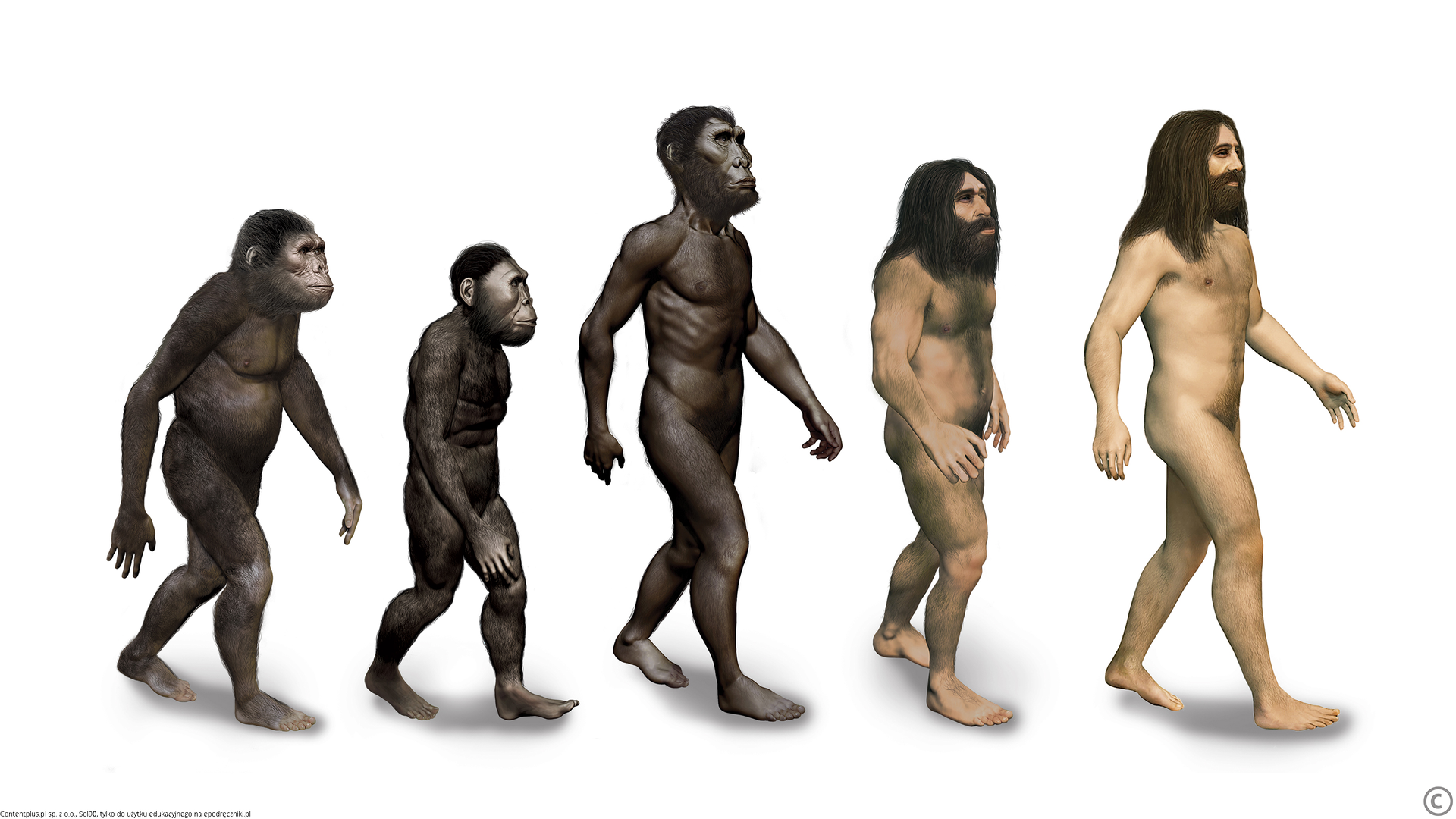
Watch the video and think about how hunting could affect the development of communication between early humans.

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Film przedstawia skoordynowaną akcję ataku na stado mamutów przeprowadzoną przez pierwszych ludzi. Akcja dzieję się w skalistym wąwozie. Ludzie najpierw oddzielają najmniejsze zwierzę ze stada, wchodząc między zwierzęta i wymachując włóczniami. Zapędzają swoją ofiarę w ślepy zaułek. Ludzie stojący na szczycie wąwozu zrzucają skały na zapędzone zwierzę, które traci przytomność i zostaje dobite przez ludzi.
Among the features below, mark those that are characteristic of the Neolithic revolution.
- leading a sedentary lifestyle
- mammoth hunting
- living in nomadic groups
- ability to ignite fire
- the ability to grow cereals
- ability to breed animals
- ability to make tools
- movement for the purpose of seeking food
Familiarize yourself with information about the prehistoric city of Catal Huyuk, then consider what elements it lacks in comparison to the modern city, and why.
Based on the lessons and your own knowledge, divide the statements into true and false.
The earliest species of our genus was <em>Homo habilis.</em>, Our human ancestors learned to use one of the most important inventions of humankind, fire, around a million to half a million years ago., The Neolithic revolution is a change that resulted in sedentary lifestyle, ability to breed animals and cultivate the land (cereals)., A man from Ötzi was found in the Himalayas., Pleistocene is called the Green Age., One of the most beautiful rock paintings can be found in the Postojna Cave in Slovenia., The creator of the theory of species evolution is the British naturalist Charles Darwin., First people lived in the areas of Asia and Australia., Prehistory is the first historical period., Venus of Willendorf is an example of the prehistoric ideal of womanhood and probably presents the first female deities.
| TRUE | |
|---|---|
| FALSE |
Keywords
prehistory, Neolith, revolution, hominids, Pleistocene
Glossary
Prehistoria – okres najdawniejszych dziejów człowieka do czasu wynalezienia pisma około 4000 r. p.n.e. Nie zalicza się do epok historycznych i jest najdłuższym okresem w dziejach ludzkości.
Hominidy – nazywane też człowiekowate, rodzina ssaków o dużej inteligencji i skłonności do pionowej, dwunożnej postawy oraz umiejętności wytwarzania i używania narzędzi.
Pięściak – prehistoryczne narzędzie wykonane najczęściej z krzemienia lub innych twardych skał o owalnym kształcie, służące do cięcia.
Malarstwo jaskiniowe – nazywane często malarstwem naskalnym. Są to malowidła powstałe w czasach prehistorycznych na ścianach jaskiń przedstawiające najczęściej zwierzęta. Najsłynniejsze przykłady można znaleźć w Lascaux we Francji i Altamirze w Hiszpanii.
Ewolucja – to długotrwały proces przemian, które dokonują się w obrębie gatunku w kolejnych pokoleniach jego istnienia. Jego podstawową cechą jest eliminacja poprzez selekcję naturalną.
Plejstocen – epoka istnienia ziemi trwająca ponad 2,5 mln lat, nazywana potocznie epoką lodowcową, ze względu na lądolody, które pokrywały wtedy znaczą część świata. Podczas jej trwania rozwinął się i wykształcił człowiek rozumny z rodzaju Homo.
Neolit – zwany też młodszą epoką kamienia, to okres w dziejach świata (9000‑3500 lat p.n.e.), którego charakterystyczną cechą było pojawienie się rolnictwa, hodowli zwierząt i osiadły tryb życia ludzi – rewolucja neolityczna.
Rewolucja neolityczna – zmiany w życiu ludzi zachodzące w neolicie, których najważniejszym efektem był osiadły tryb życia, umiejętność hodowli zwierząt i uprawy roli (zbóż).
Żyzny Półksiężyc – żyzny pas ziemi w kształcie łuku rozciągający się od Zatoki Perskiej (Mezopotamii) do półwyspu Synaj (Egiptu). Był powstania pierwszych stałych osad ludzkich i miejscem narodzin pierwszych cywilizacji.
Megality – wielkie, prehistoryczne budowle kamienne, występujące na obszarze całego świata z epoki neolitu, rzadziej brązu, o charakterze kulturowym, grobowym i prawdopodobnie astronomicznym.