Renaissance in Europe
to explain the terms: renaissancerenaissance and humanismhumanism;
to define the characteristics of the Renaissance period;
who the following figures were: Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, Jan Gutenberg;
the impact of the invention of Jan Gutenberg on lives of people.
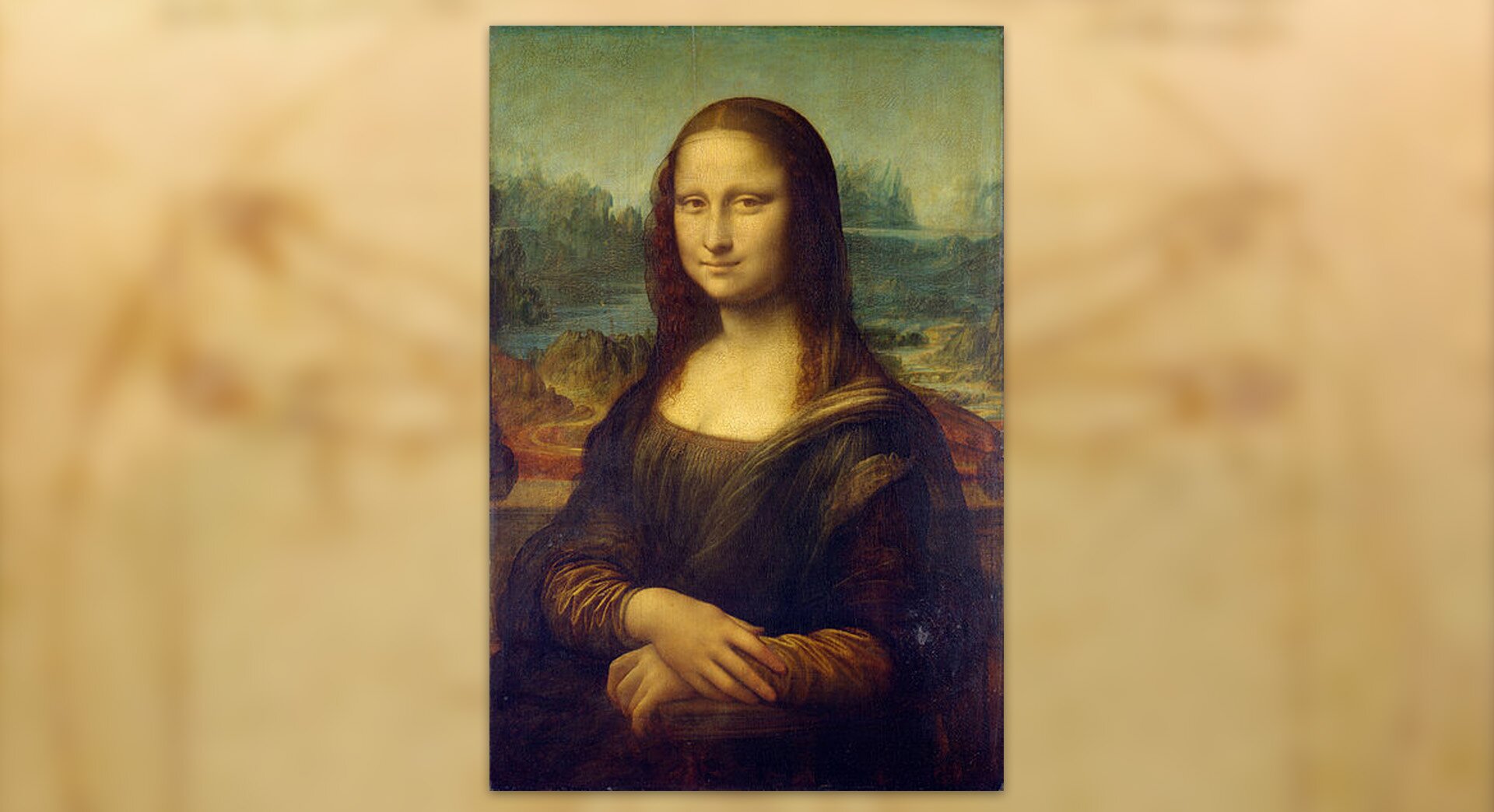
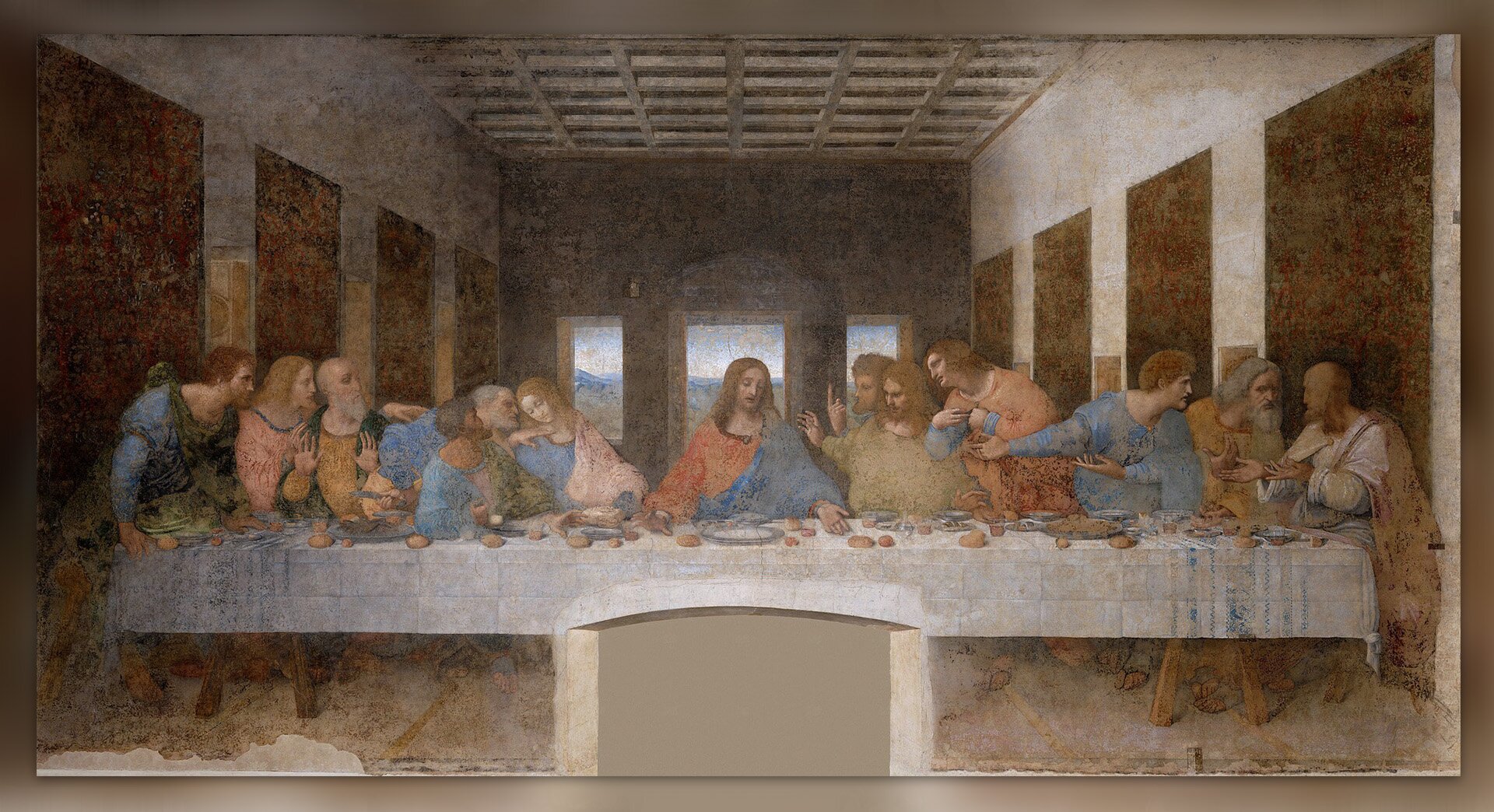
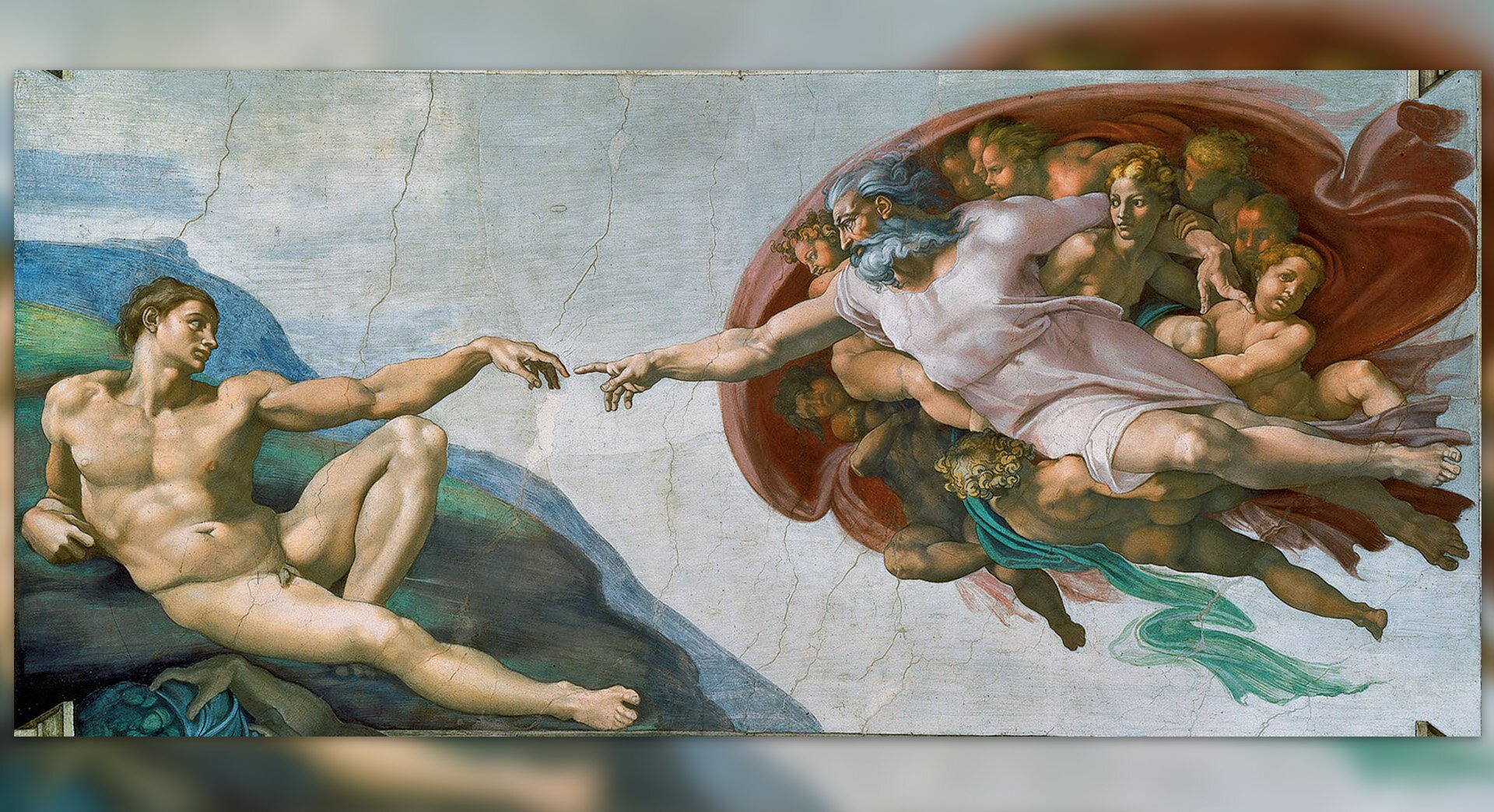
In the 13th century, interest in antiquity began to grow in Italy. This marked the beginning of the Renaissance, i.e. the rebirth of ancient culture. It was referred to in architecture, sculpture, painting and literature. Man became the focus of interest for artists and thinkers. With time, Renaissance ideas became popular throughout Europe (Renaissance reached its peak at the end of the 15th century and in the 16th century). The invention of printprint by Jan Gutenberg had a huge impact on the dissemination of these ideas. His first book to be printed was the Bible. The most important figures of the Renaissance include: Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, Rafael Santi and Erasmus of Rotterdam.
Read the text below and think about the answers to the following questions:
Why was the new era called Renaissance?
How it differed from the previous one – the Middle Ages?

In 1453 Constantinople, the capital of the Eastern Roman Empire (called Byzantium), was conquered by the Turks. This meant the end of this state’s existence. Many Byzantine scholars left their homeland and moved to safer Italy. The scholars brought ancient Roman and Greek manuscripts and scientific treatises with them. This aroused a fascination with antiquity in Italy. It became fashionable to study Greek philosophy and read Roman works in Latin. The ancient architecture was admired. The result was an extraordinary development of art modeled on antique works. For this reason, a new era in the history of culture was called a Renaissance, literally meaning „Rebirth” in French.
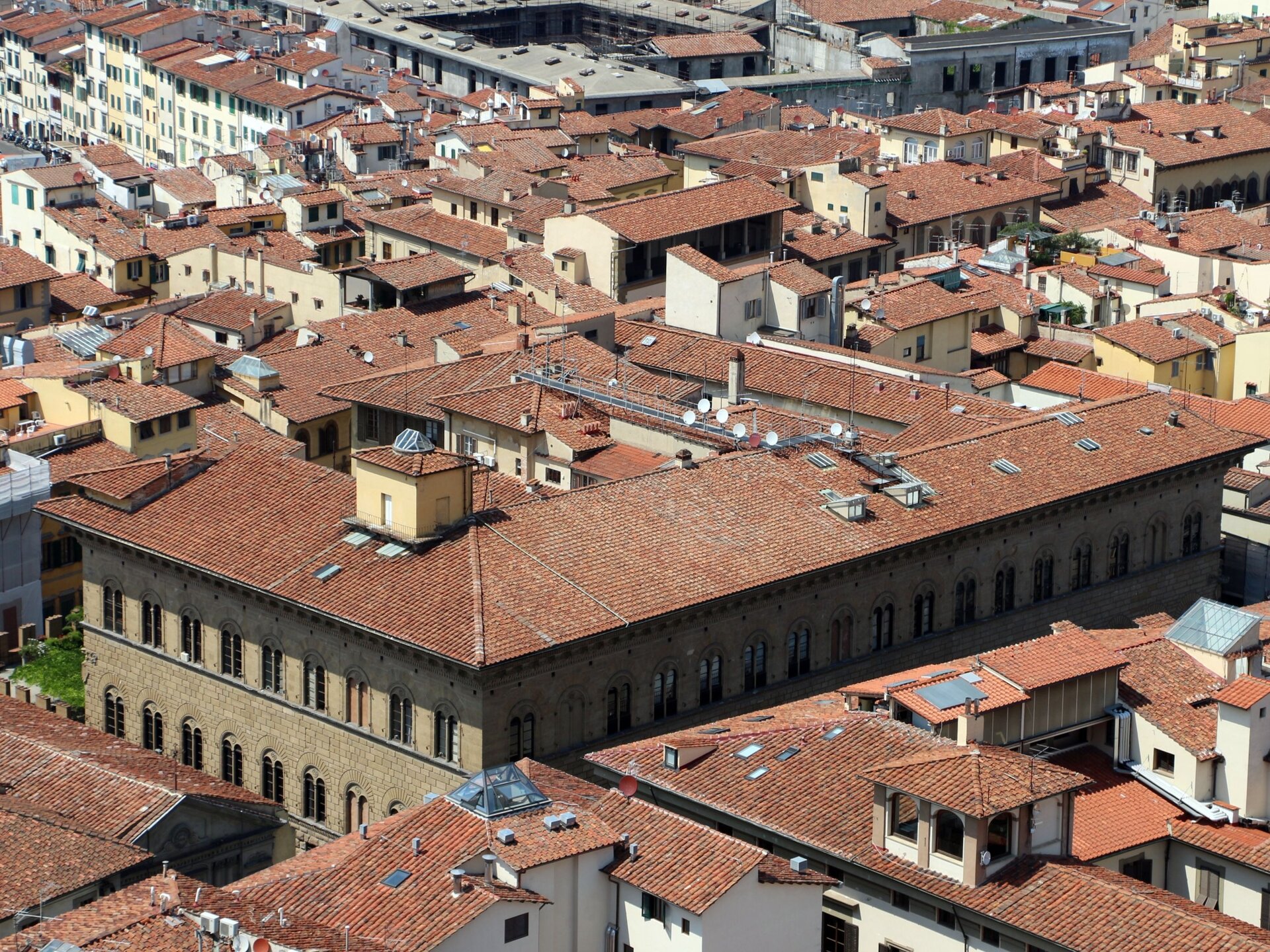
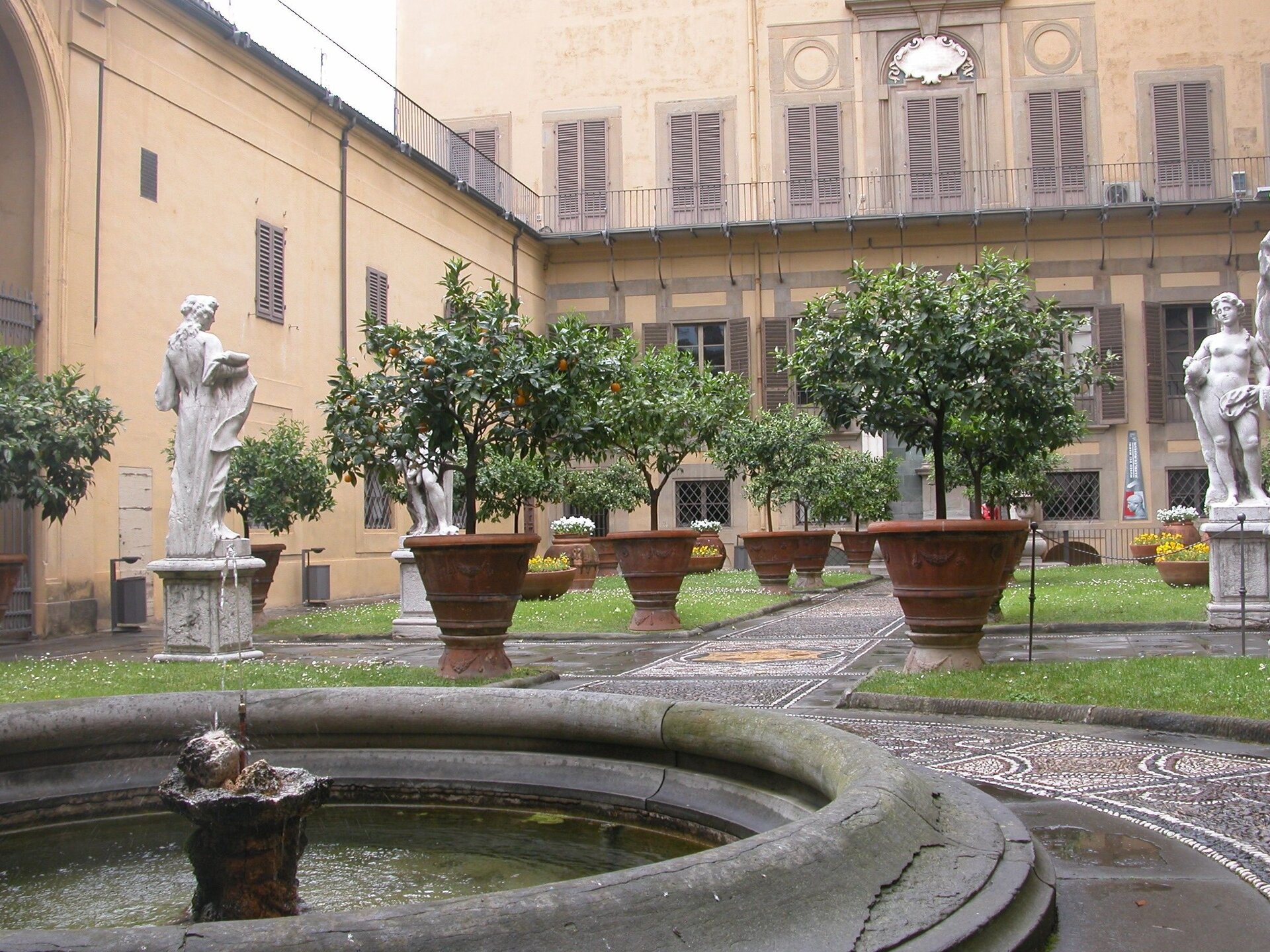
Indicate the features of the Renaissance Palazzo Medici. Tick the correct answers.
- Tall windows with sharp arches.
- Almost flat roof.
- A rectangular courtyard decorated with a fountain, sculptures and exotic plants.
- Moat and other elements presenting defensive features.
- The windows similar in shape to rectangular ones, topped with gentle arches.
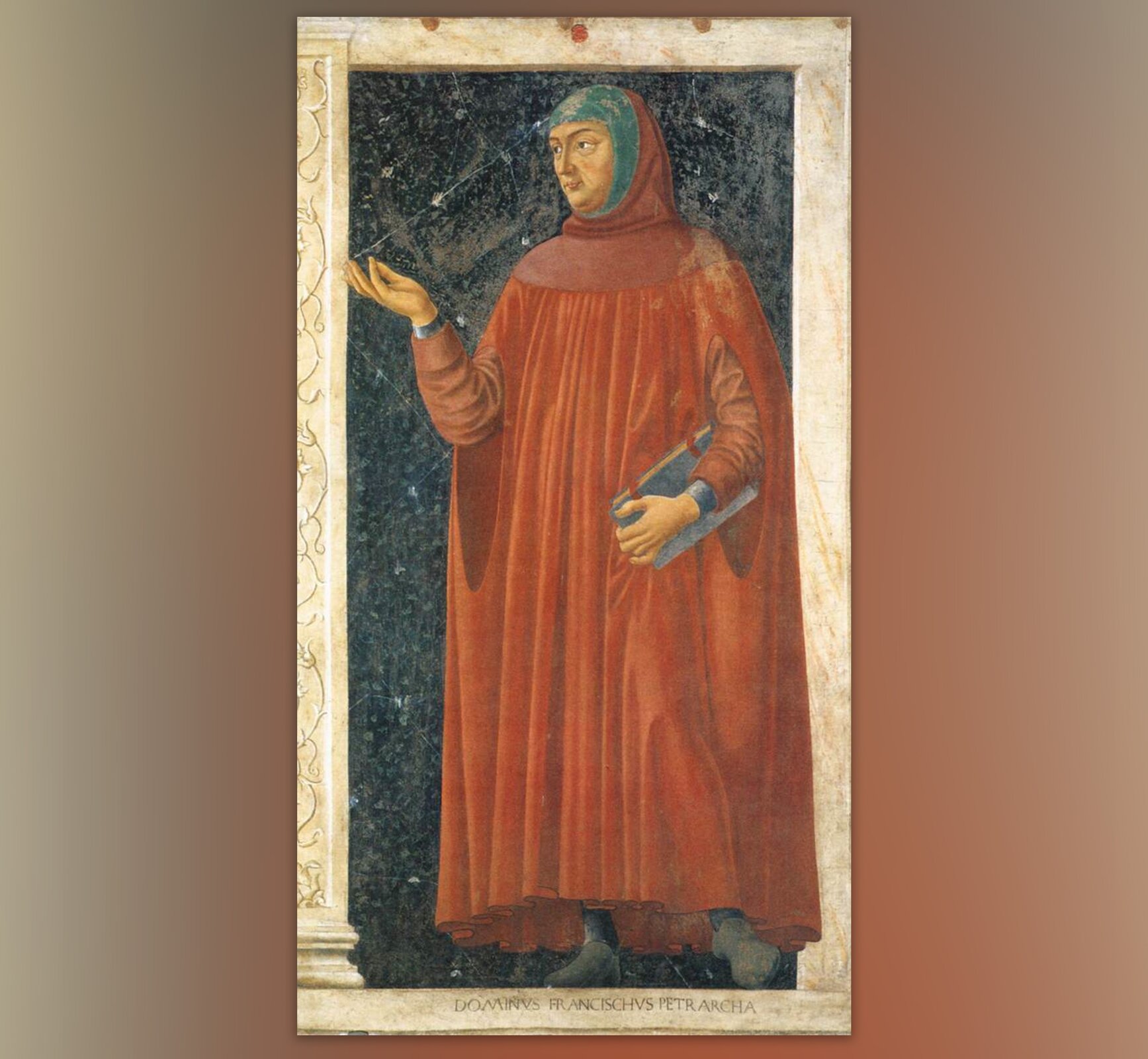
The illustrations below depict two Italian writers and humanists. How can you know that the presented men are writers?
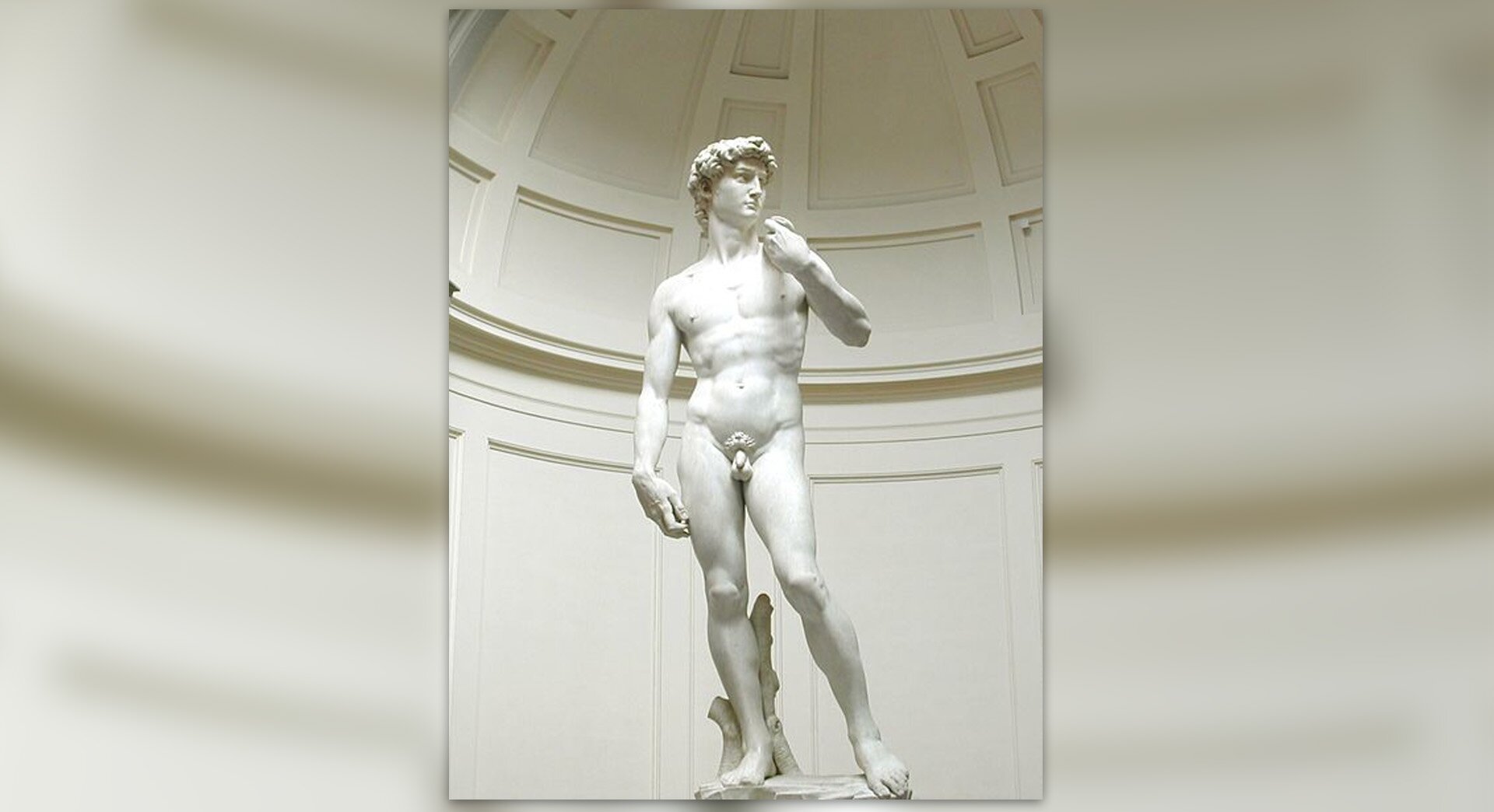
Artists of the Renaissance period considered ancient works and the harmony of the human body to be the models of beauty. They tried to combine these features and refer to ancient art in their works. You have already learned about two great artists of the Renaissance era – Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo and their wonderful works. It was not only them, however, who left their mark on the history of their time.
The Renaissance artists were also inspired by biblical themes. Read the information about the painting „The Tower of Babel” by Pieter Breugel the Elder.
Find in the Internet and watch the educational film devoted to Pieter Bruegel's painting “The Tower of Babel”. What is the place of man in the human work of creation that is to be equal to God? What impression has this painting made on the viewers? What have they noticed?
Count how many "a" fonts you need to assemble and print the following sentence at one time:
- 7
- 6
- 5
- 4
Which of the sentences are true, and which are false?
{true}The fall of Constantinople is considered the end of antiquity.{/true}
{true}Athens’ Parthenon became one of the models for Renaissance architects.{/true}
{true}The printing font was invented by Jan Gutenberg.{/true}
{false}The Renaissance is also called enlightenment.{/false}
{true}Michelangelo is the author of the sculpture of David.{/true}
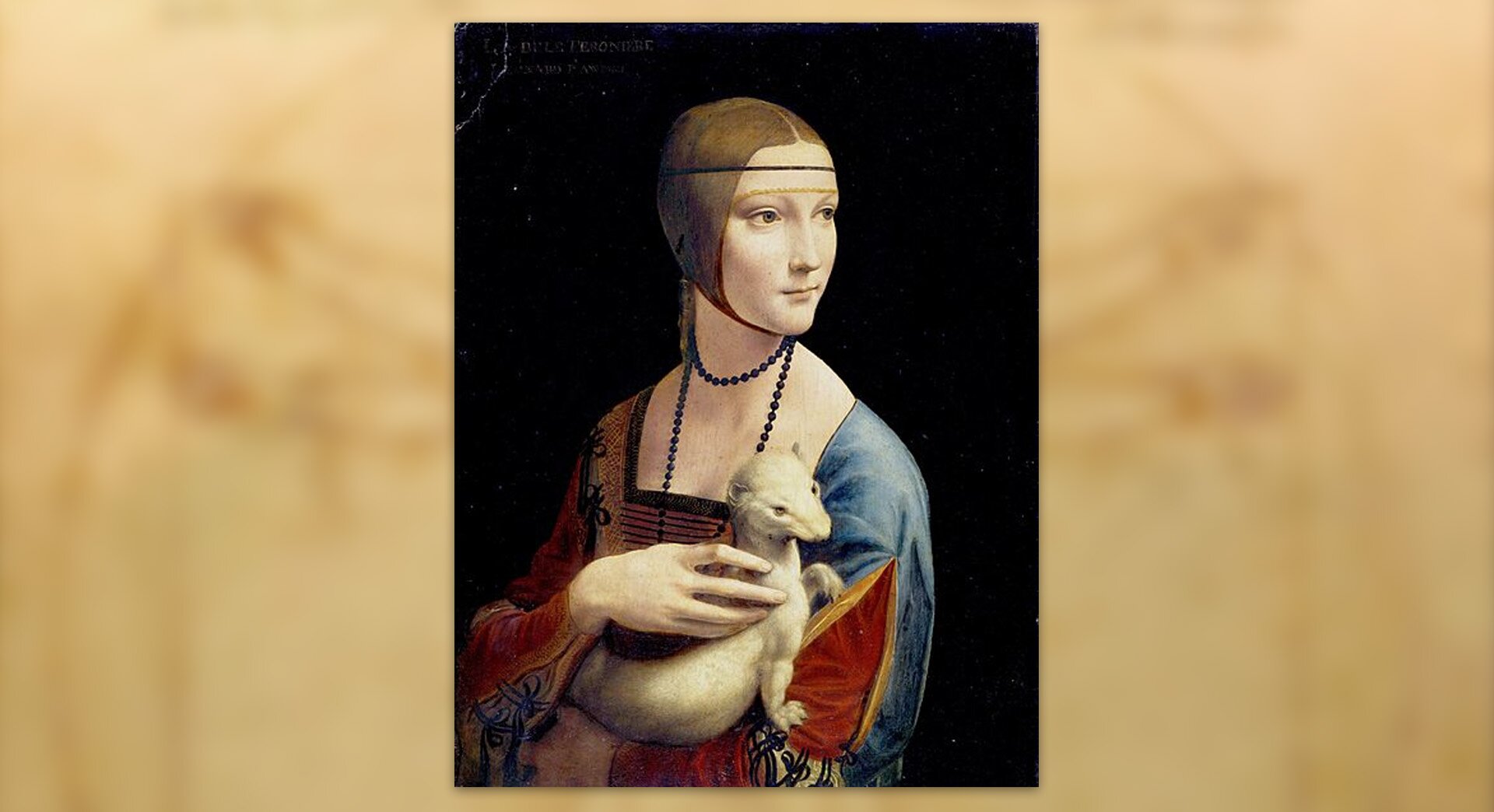
{false}The Lady with an Ermine was painted by Raphael Santi.{/false}
{false}All those who could read Latin were called humanists.{/false}
{true}The motto of the humanists was " I am a human being, I think nothing human alien to me".{/true}
Keywords
renaissance, print, Michelangelo, Jan Gutenberg
Glossary
Bizancjum – inaczej Cesarstwo Wschodniorzymskie, państwo ze stolicą w Konstantynopolu, istniejące po upadku Cesarstwa Zachodniorzymskiego. Istniało do 1453 roku kiedy upadło przez podbój Turków.
renesans – epoka nazywana odrodzeniem sztuki i nauki, trwająca w Europie od XV do połowy XVII wieku (w niektórych krajach europejskich). W czasie jej trwania nastąpił wzrost zainteresowania antykiem i ludzkim ciałem.
kopuła – element architektoniczny o kształcie półkolistym charakterystyczny dla epoki renesansu.
mecenat – opieka wpływowych i bogatych miłośników nauki i sztuki nad artystami. Wspomagają oni finansowo artystów zatrudniając ich w swoich posiadłościach lub zlecając tworzenie dzieł sztuki, np. obrazów, rzeźb.
humanizm – główny prąd intelektualny epoki renesansu powstały we Włoszech w XV wieku. Zakładał, że człowiek i jego ziemskie życie jest najwyższą wartością.
człowiek renesansu – określenie osoby wszechstronnie wykształconej, posiadającej rozległą wiedzę z różnych dziedzin nauki.
druk – wielokrotne odbijanie, powielanie obrazu i treści na materiale, np. papierze. Nazywa się tak również każdą kopię czy odbitkę.
czcionka – pojedynczy znak drukarski dający w druku odbitkę litery, cyfry lub znaku.










