Bookkeeping and preparing tax statements of the company in agribusiness
Financial analysis of a company
1. Film in the standard version.
2. Film with subtitles.
3. Film with subtitles and pauses. Listen and repeat after the speaker.
4. Film with subtitles and narration.
Answer the question based on the film “Company financial analysis” Po obejrzeniu filmu połącz polskie terminy z ich angielskimi odpowiednikami
sytuacja finansowa, bilans, sprawozdanie finansowe, kapitał, rok obrachunkowy, aktywa, zysk, koszty, pasywa, kapitał własny
| financial status | |
| financial statements | |
| accounting year | |
| balance | |
| assets | |
| liabilities | |
| capital | |
| profit | |
| costs | |
| private equity |
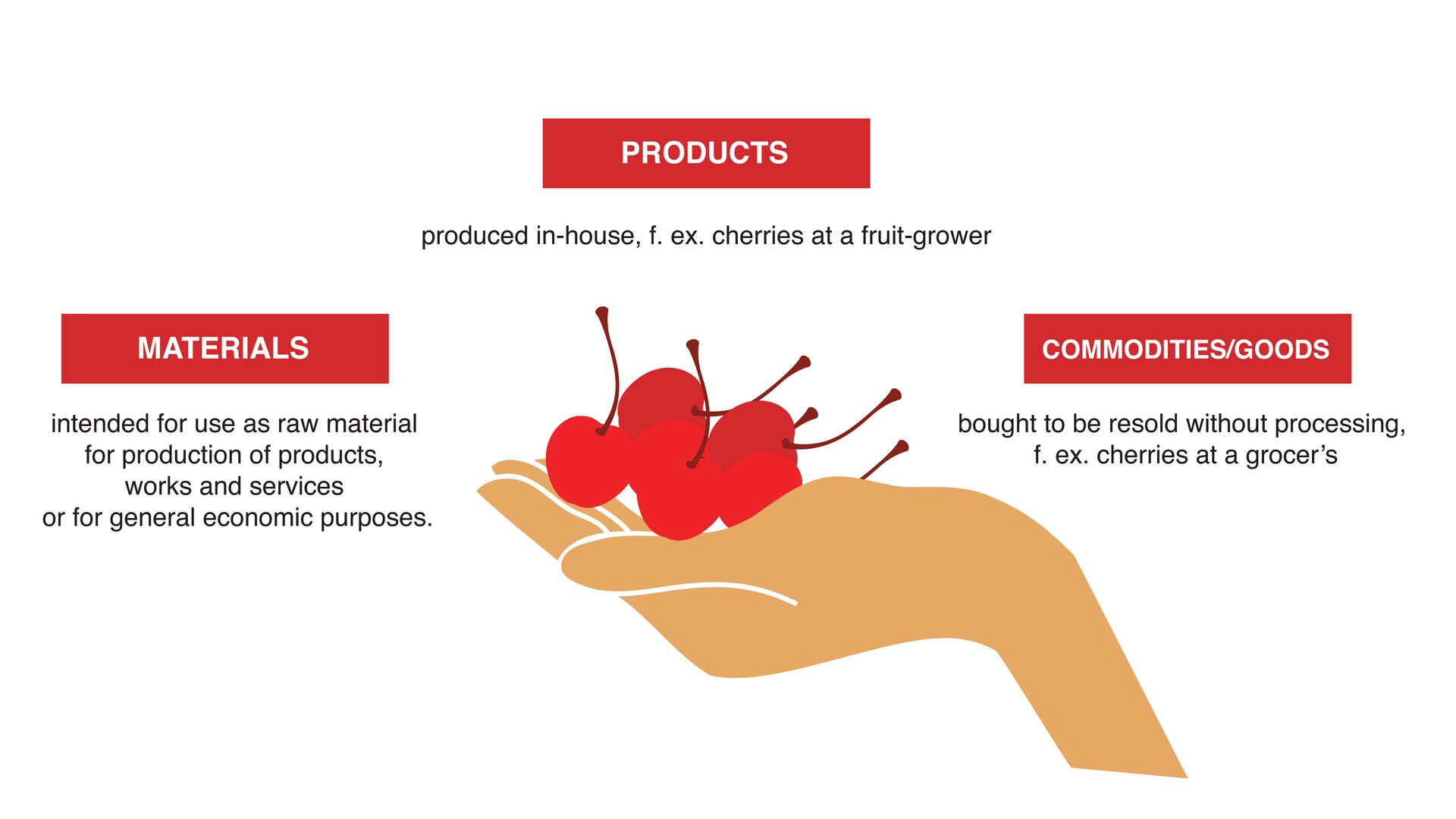
Calculation of pork livestock production

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
moduł 7.3, Direct costs are costs that without a doubt can be classified to a specific business activity and their amount is proportional to the production scale. In the case of pork livestock production, direct costs include purchased feed, costs of feed produced on-farm with a commodity potential, veterinary services and purchase of a piglet. Income are the finances coming into the company from sale of products, goods, net services, (without VAT) or other operations which are a part of the basic business activities of the company within a specific accounting period. Direct surplus - it is the production value less the direct costs incurred during that production. Indirect costs mean those costs that cannot be assigned to a specific business activity. Indirect costs in the production of pork livestock include: amortization, which is the depreciation of fixed assets, costs of paid work and other costs, f. ex. insurance costs, taxes, energy. Total costs are a sum of direct and indirect costs. Net agricultural income - is a direct surplus minus the direct cost. The workload of the farmer is not included in the calculation. The remuneration for their work is a part of the agricultural income.
Familiarize yourself with the animation and match the Polish terms to their English equivalents. Po zapoznaniu się z animacją, połącz polskie terminy z ich angielskimi odpowiednikami
pasz własnych potencjalnie towarowych, Nadwyżka bezpośrednia, Dochód rolniczy netto, usługi netto, Koszty całkowite, dobra, Przychód, skala produkcji, Koszty pośrednie, koszty bezpośrednie
| direct costs | |
| production scale | |
| feed produced on-farm with a commodity potential | |
| Income | |
| goods | |
| net services | |
| Direct surplus | |
| Indirect costs | |
| Total costs | |
| Net agricultural income |
The company’s assets and their financing sources
Financial statement
The hypertext is a description of financial statement elements
Financial statement consists of three basic elements: balance, profit and loss statement and additional information.
Balance shows the assets in the company possession and the financing sources of those assets (liabilities).
Profit and loss statement shows income, costs, profit and loss. The elements of the profit and loss statement must be shown in order and way specified by the Act. Income is divided into:
- income from operationsoperations,
- other operational income
- financial income.
Income from operations included:
- income from sales of products -finished goodsfinished goods, intermediate productsintermediate products or services and work, income from material sales
- occurring when unused reserve of materials is sold.
Costs are divided into:
- operational costs,
- other operational costs,
- financial costs.
Operational costs include:
- consumption of materials and energy,
- remuneration (but only for employees connected with production),
- amortization,
- outsources servicesoutsources services,
- social securitysocial security.
Other operational income and costs are connected with:
- sale of the fixed assetsfixed assets,
- intangible assets,
- with damagesdamages,
- fines,
- with donationsdonations.
The company can also conduct financial activitiesfinancial activities. Financial income consist of:
- dividendsdividends,
- interest rates on investmentinvestment accounts and granted loans,
- exchange gainsexchange gains
Positive difference between income and costs means that there is a profit. If the difference is negative, then the company incurred a loss.
The inspection report
Text contains recommendations regarding the document workflow in the company. Due to finding some irregularities during an inspection, the inspecting body has issued recommendations that can be used both in traditional and modern (electronic) document workflow.
Due to finding irregularities in document workflowdocument workflow andstoragestorage in your company, the following rules are recommended:
- saving documents in one specific area ;
- setting up one method for naming documents. Additionally, to facilitate the viewing of documents, it is best to create widely accepted keyphrases - shortcuts/symbols - in order to classify in a faster and easier way:
- adding the date to the document name, - proper organization of documents
-creating one folder for documents relating to one particular area,
- creating backup copies of documents. Keeping back‑up copiesback‑up copies in the so‑called cloud should also be considered.
The dynamic development of your company allows to predict that the number of documents entering your company will be increasing. Therefore, we recommend purchasing a professional software or application supporting theelectronic document workflowelectronic document workflow in the company.
The additional benefits are:
lowering the operational costsoperational costs,
improving work in the company,
optimization of information workflowinformation workflow,
process monitoringprocess monitoring at all stages, minimizing the risk of their loss,
and saving time. The workplace is obliged to keep in the archive for 50 years the personal records, payrollspayrolls, payroll cardspayroll cards, contractscontracts and billsbills for commissioned workcommissioned work, with social security, which is used to calculate the pensionpension or retirement pension basisretirement pension basis. Documents which are not accounting documentsaccounting documents can be stored for 5 years.
The market situation for sugar
Farmers talk about the perspectives of sugar beet cultivation in the context of foreign trade. The farmers debate about whether or not they should increase the area of beer cultivation as the price of beet roots is falling. It might be due to an increase of imported sugar from South America, made from sugarcane.The farmers conclude that the situation on the international markets has a direct influence on their decisions.
- Good morning neighbour.
- Morning. What’s new?
- I’m just returning from the meeting of the sugar beet producers groupproducers group.
- What perspectives does that trade have?
- It isn’t good. The national production of sugar is still on a downward trend.
- What’s the reason for this?
- It is the effect of an increase of cane sugar importedimported from South America, the price of which is competitivecompetitive towards beet sugar.
- Why?
- The workforceworkforce is cheaper there and the manufacturing costsmanufacturing costs of the raw material are different.
- And you have invested in new combine harvester…
- Yes, I took out a loantook out a loan, and the machine is only working for a few days a year.
- So its value is decreasing despite that it is not exploited.
- Yes, its moral wearmoral wear is greater than itswear and tearwear and tear.
- Maybe you should offer some harvesting services?
- I did that last year and the income was smaller than the fuel, repair, servicing and insurance costs. That activity was not profitable and I had incurred a loss.
- Did you do it yourself?
- No, as a part of a business activity, I have hired a combine harvester operator using a contract for mandatecontract for mandate.
- Isn’t conducting business activity complicated?
- No, finances and documentation are handled by my daughter who has an accounting office.accounting office. She handles accountancyaccountancy, personal and property insurance, financial liabilities,and taxes.
- Is she handling it well?
- Perfectly! Not long ago, I had an inspection from the National Labour InspectorateNational Labour Inspectorateand it turned out that all of the documents regarding employment and salary calculation were in perfect order.
- And what does your son do?
- He is also supporting my business. He takes care of marketingmarketing, customer relationscustomer relations and raw material deliveries.
- You have turned a small farm into a real business!
- Actually it is just a small family business, but I have plans for its further development.
After reading the hypertext document translate the words and expressions.Po przeczytaniu dokumentu hipertekstowego przetłumacz słowa i zwroty
grupy producentów, kontakt z klientem, koszty wytwarzania, siła robocza, umowa-zlecenie, zaciągnąć kredyt, branża, księgowość
| producers group | |
| trade | |
| workforce | |
| manufacturing costs | |
| took out a loan | |
| contract for mandate | |
| customer relations | |
| accountancy |
Match the words with their definitions Dopasuj wyrazy do definicji
treasury bonds, post-inspection report, wear and tear, balance sheet accounts, total costs, company shares, payables, profit and loss statement, production value, balance, opening balance, foreign capital, income, accounting ledger, current assets, direct surplus, account balance, intangible assets, closing balance, turnover, fixed assets, opening balance, indirect cost, the right of perpetual usufruct of land, closing balance, net agricultural business, direct surplus
………. ………… – is the production value from 1 hectare of crops or of one animal less the direct costs incurred during that production. ..............................................................................
……….. ……… – is the sum of direct and indirect costs. ..............................................................................
………. ……….. shows the income, costs, profit and loss. ..............................................................................
……… ……….. is a basic tool used to record business events. ..............................................................................
…………….. is the sum of entries on one side of the statement. ..............................................................................
………. ………… is the difference between turnovers on both sides of the account ..............................................................................
………… …………. are the accounts used to record the elements of the balance. ..............................................................................
………. ……….. is the balance on the account at the end of a period. ..............................................................................
………. are finances entering the company from the sale of products, goods, net services (without VAT), or other operations which are a part of the basic business activities of the company within a specific accounting period. ..............................................................................
Basic information about account ledgers together with their division.
On the basis of the audio-visual material, choose the right answer. Na podstawie materiału audio-video dokonaj właściwych odpowiedzi
| Prawda | Fałsz | |
| An account ledger is a basic tool used for recording business events. | □ | □ |
| Account ledgers are graphically represented by the letter U. | □ | □ |
| The right side of the statement is called “Debit,” Dr in short. | □ | □ |
| Recording an operation on the Cr side is called debiting or charging the account. | □ | □ |
| The sum of entries on one side of the account is called turnover. | □ | □ |
| The account balance is the difference between turnovers on both sides of the statement. | □ | □ |
| Opening balance (OB in short) is the balance on the account at the end of a given period. | □ | □ |
| Accounts used for recording the elements of the balance are called balance sheet accounts. | □ | □ |
| Debit accounts are used to record the values of assets. | □ | □ |
Pictures
Familiarize yourself with the content of the picture.
Translate the names of individual elements of profit and loss statement visible on the figure into Polish.

Look at the photo and read the terms used in the accounting software

Game

Zasób interaktywny dostępny pod adresem https://zpe.gov.pl/a/DNVBjDE0V
Dictionary
saldo konta
konto księgowe
księgowość
dowód księgowy
biuro rachunkowe
rok obrachunkowy
amortyzacja
składnik aktywów
aktywa, składniki majątku
kopia zapasowa
bilans
konto bilansowe
rachunek
zdarzenie gospodarcze
operacja gospodarcza
kapitał
obciążenie konta
saldo końcowe
prace zlecone
majątek przedsiębiorstwa
konkurencyjny
umowa
umowa‑zlecenie
koszt
kredyt
konto pasywne
uznanie konta
aktywa obrotowe
kontakty z klientami
odszkodowania
debet, ciężar konta, winien
konto aktywne
koszt bezpośredni
nadwyżka bezpośrednia
dywidenda
przechowywanie dokumentów
obieg dokumentów
darowizna
elektroniczny obieg dokumentów
różnica kursowa
pasze własne potencjalnie towarowe
działalność finansowa
sprawozdanie finansowe
sytuacja finansowa
wyroby gotowe
aktywa trwałe, środki trwałe, majątek trwały
dobro konta
kapitał obcy
dobra
import
przychód
koszt pośredni
przepływ informacji
wartości niematerialne i prawne
półprodukt
inwestycja, lokata
pasywa
składnik pasywów
koszt wytwarzania
marketing
zużycie moralne
dochód rolniczy netto
usługa netto
saldo początkowe
działalność operacyjna
koszty operacyjne
usługa obca
praca najemna
zobowiązania
lista płac
karta wynagrodzeń
renta
kapitał własny
monitorowanie procesów
grupa producentów
skala produkcji
wartość produkcji
zysk
rachunek zysków i strat
rentowność
należności
czynsz
zapasy
wymiar emerytury
okres rozliczeniowy
kapitał podstawowy
socjalne
ubezpieczenia społeczne
kapitał zapasowy
zaciągnąć kredyt
rzeczowe aktywa trwałe
Państwowa Inspekcja Pracy
koszty całkowite
branża
obrót
podatek VAT
zużycie fizyczne
siła robocza





