Hydrocarbon derivatives – a repetition lesson
Links to the lessons: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
Links to the abstracts: 11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66
to ask questions and answer your friends' questions about hydrocarbon derivatives.
to consolidate the material from the lessons: „Alcohols – structure”, „Alcohols – properties”, „Alcohols – effects on the human body”, „Polyhydric alcohols”, „Carboxylic acids – properties”, „Esters – structure and properties”;
to consolidate the vocabulary related to the theme of hydrocarbon derivatives.
Before you begin solving the exercises, review abstracts „Alcohols – structure”, „Alcohols – properties”, „Alcohols – effects on the human body”, „Polyhydric alcohols”, „Carboxylic acids – properties”, „Esters – structure and properties” to recall the most important information and vocabulary. Then you will be able to check your knowledge. Good luck!
Before the lesson
Arrange a crossword, whose main password will be related to the content of lesson "Polyhydric alcohols".
Repetition
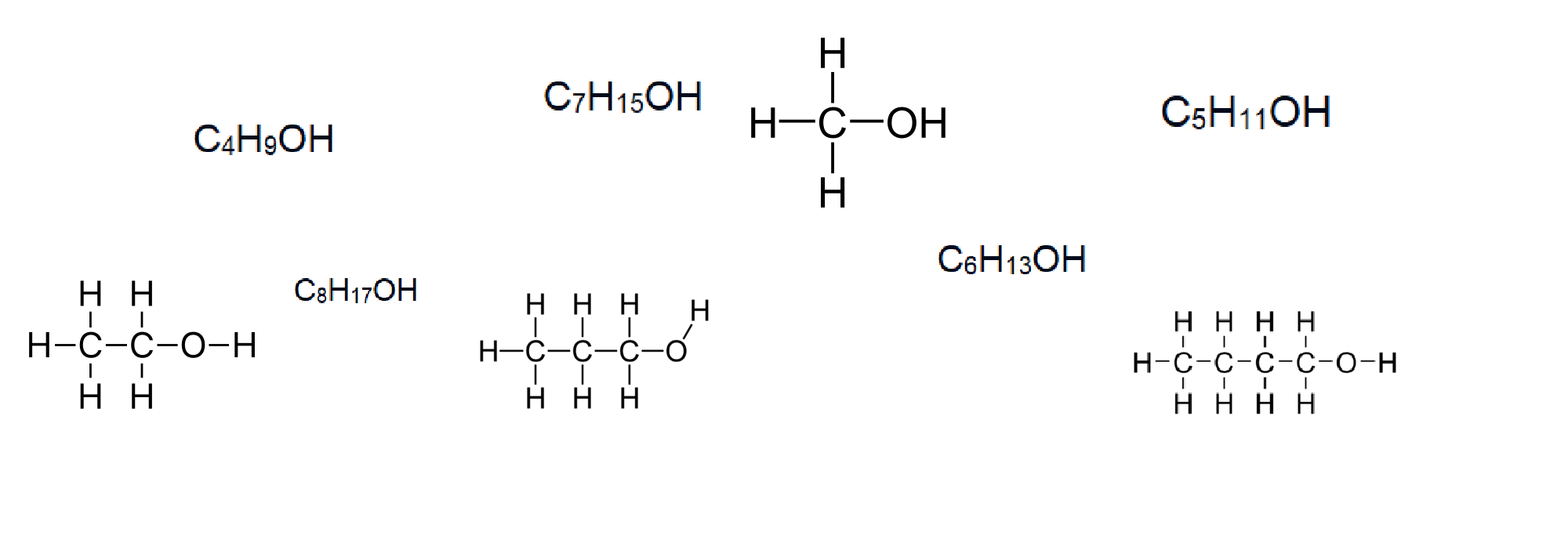
Look at the formulas on the board. What are the chemical compounds? What do you know about their hut? Place information on the board.
Listen to the recording „Alcohols - effects on the human body” and write down questions you could ask your friend or colleague to check if he understood the text read. Also note the expected answers.
Select properties for ethanol.
- It is flammable, boiling point of 64.7oC.
- Mix with water without restrictions.
- It is alkaline due to the presence of hydroxyl group.
- Has a characteristic, sharp smell.
- Burns blue, yellow and smoky flame.
- It is a white liquid.
- Has a sharp taste.
Listen to the recording „Carboxylic acids – properties” and write down questions you could ask your friend or colleague to check if he understood the text read. Also note the expected answers.
Complete a multiple-choice test question for the lesson "Esters – structure and properties".
Question: ...
- ...
- ...
- ...
- ...
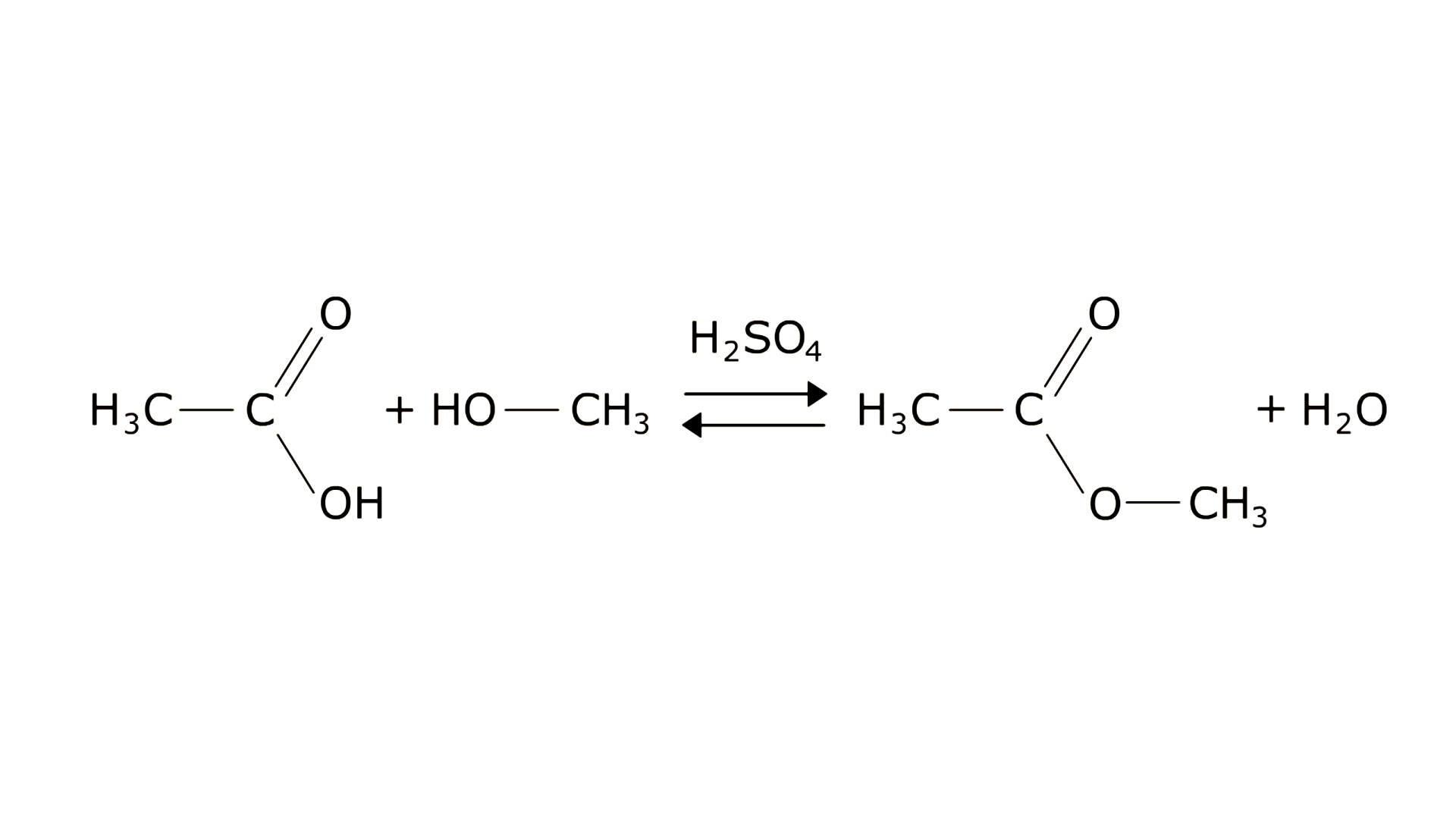
Analyse the esterification reaction presented below and name the substances involved in it.
Do you know how fragrant esters smell? Match the fragrance to the substance name.
the smell of rum, the smell of raspberries, the smell of jasmine, the smell of apples, the smell of pineapples, the smell of orange, the smell of bananas
| buthyl butyrate | |
| methyl butyrate | |
| benzyl formate | |
| octyl acetate | |
| ethyl formate | |
| isobuthyl formate | |
| amyl acetate |
Match the pairs: English words and Polish definitions.
jedna tysięczna pewnej całości; oznaczany symbolem ‰, przemiana glukozy pod wpływem enzymów wytwarzanych przez drożdże; jej produktami są alkohol etylowy i tlenek węgla(IV), alkohol etylowy z dodatkiem substancji o przykrym zapachu i smaku, nienadający się do spożycia; zabarwiony na fioletowo lub czerwono;, zjawisko fizyczne, które polega na zmianie objętości roztworu podczas mieszania jego składników, pochodne węglowodorów, w których co najmniej jeden atom wodoru zastąpiono grupą hydroksylową, choroba alkoholowa, uzależnienie od picia alkoholu, wodny roztwór alkoholu etylowego o stężeniu około 96%
| alcohols | |
| alcoholic fermentation | |
| denatured alcohol | |
| volume contraction | |
| rectified spirit | |
| alcoholism | |
| promil |
Summary
The alcohol fermentation products are ethanol and carbon dioxide.
Methanol and ethanol contain one functional group in their molecules. These are monohydric alcohols.
Monohydric alcohols are compounds in which one hydrogen atom has been replaced by a monovalent group – OH.
Methanol and ethanol are flammable substances. These are subject to complete and incomplete combustion reactions.
Methanol and ethanol have many common physical properties and are therefore difficult to distinguish. Methanol is a poison, and ethyl alcohol has a negative effect on the human body.
Alcohols have many applications.
Alcohols dissolve well in water.
The pH of aqueous solutions of alcohols is neutral.
In Poland, it is prohibited to buy and consume ethyl alcohol by people under 18 years of age.
Glycerol and glycerine are common names of the same chemical compound – propanetriol.
The glycerol molecule consists of three hydroxyl groups.
Glycerol is a thick oily, colourless and odourless liquid with a sweet taste. It is not a poisonous substance.
Glycerol is widely used in the cosmetics, food and textile industries.
Carboxylic acids react with hydroxides, metals and metal oxides, to form salts.
The reaction of aqueous solutions of carboxylic acids that have short carbon chains, and the electrical conductivity, are evidence of electrolytic dissociation.
Pure acetic acid is a colourless, corrosive liquid. It is hygroscopic (it absorbs moisture from the air).
At temperatures below 16°C, it forms crystals that resemble ice in appearance. It is also called glacial acetic acid.
Acetic and formic acids dissolve well in water.
Esters are an important group of compounds in living organisms.
Esters are obtained as a result of esterification reaction, i. e. reaction of carboxylic acids with alcohols.
In the esterification reaction sulfuric acid acts as a catalyst, i. e. accelerates the reaction process.
General formula for esters is RIndeks dolny 11COORIndeks dolny 22, and the characteristic group is the ester group –COO–.
Esters are slightly soluble in water, but dissolve well in organic solvents and are therefore used as solvents for paints and varnishes.
Some esters have a pleasant smell and these are used, among others, in the production of perfumes and essential oils.
Keywords
alcohol, hydrocarbons, monohydric alcohols, methanol, ethanol, homologous series, methyl alcohol, ethyl alcohol, positional isomerism, alcoholism, promil, chloroform, industrial spirit, glycerol, ethylene glycol, ethanediol, erythritol, polyhydric alcohol, esters, esterification, carboxylic acid
Glossary
alkohole – pochodne węglowodorów, w których co najmniej jeden atom wodoru zastąpiono grupą hydroksylową
fermentacja alkoholowa – przemiana glukozy pod wpływem enzymów wytwarzanych przez drożdże; jej produktami są alkohol etylowy i tlenek węgla(IV)
grupa funkcyjna – grupa atomów (lub atom) połączona z łańcuchem węglowym w węglowodorach; jej obecność decyduje o przynależności do danej grupy związków organicznych
szereg homologiczny alkoholi – szereg alkoholi uporządkowanych według wzrastającej liczby atomów węgla w cząsteczce; dwa kolejne związki różnią się od siebie o grupę atomów
denaturat – (spirytus skażony) – alkohol etylowy z dodatkiem substancji o przykrym zapachu i smaku, nienadający się do spożycia; zabarwiony na fioletowo lub czerwono; nie wolno spożywać denaturatu ani innego rodzaju skażonego alkoholu
kontrakcja objętości – zjawisko fizyczne, które polega na zmianie objętości roztworu podczas mieszania jego składników
spirytus – wodny roztwór alkoholu etylowego o stężeniu około 96%
spirytus drzewny – zwyczajowa nazwa otrzymywanego w wyniku suchej destylacji drewna roztworu alkoholu metylowego
alkoholizm – choroba alkoholowa, uzależnienie od picia alkoholu
spirytus przemysłowy – etanol otrzymywany w wyniku syntezy chemicznej (mieszaniny,i ); stosowany do produkcji płynu do spryskiwaczy, podpałki do grilla lub jako rozpuszczalnik w przemyśle
glicerol – nazwa zwyczajowa alkoholu o nazwie systematycznej propano‑1,2,3‑triol
gliceryna – nazwa zwyczajowa alkoholu o nazwie systematycznej propano‑1,2,3‑triol
grupa hydroksylowa – inaczej grupa wodorotlenowa
lokant – liczba przypisana atomom węgla w łańcuchu węglowym
substancja higroskopijna – substancja pochłaniająca wodę lub parę wodną z otoczenia
ocet – 6‑procentowy lub 10‑procentowy wodny roztwór kwasu octowego; na półkach sklepowych możemy znaleźć kilka rodzajów octu (jabłkowy, winny, spirytusowy)
ocet spirytusowy – wodny roztwór kwasu octowego – produkt fermentacji spirytusu
kwas octowy CHIndeks dolny 33COOH – organiczny związek chemiczny z grupy kwasów karboksylowych.
inna nazwa kwasu octowego
tlenek metalu
kwas mrówkowy HCOOH – organiczny związek chemiczny, najprostszy kwas karboksylowy.
estry – związki chemiczne zawierające grupę estrową ; powstają w wyniku reakcji estryfikacji
estryfikacja – reakcja kwasów karboksylowych z alkoholami zachodząca w obecności kwasu siarkowego(VI); w jej wyniku otrzymujemy estry