Fats - types and properties
what is the structure of esters and what is the reaction of esterification.
to classify fats in terms of origin, physical state and chemical nature;
what are the structures and properties of fats;
to design an experiment to distinguish between unsaturated fat and saturated fat.
Types and properties of fats
Consider what kind of fats you meet every day. Can you group them somehow?
We divide the fats due to their state of matter and origin.
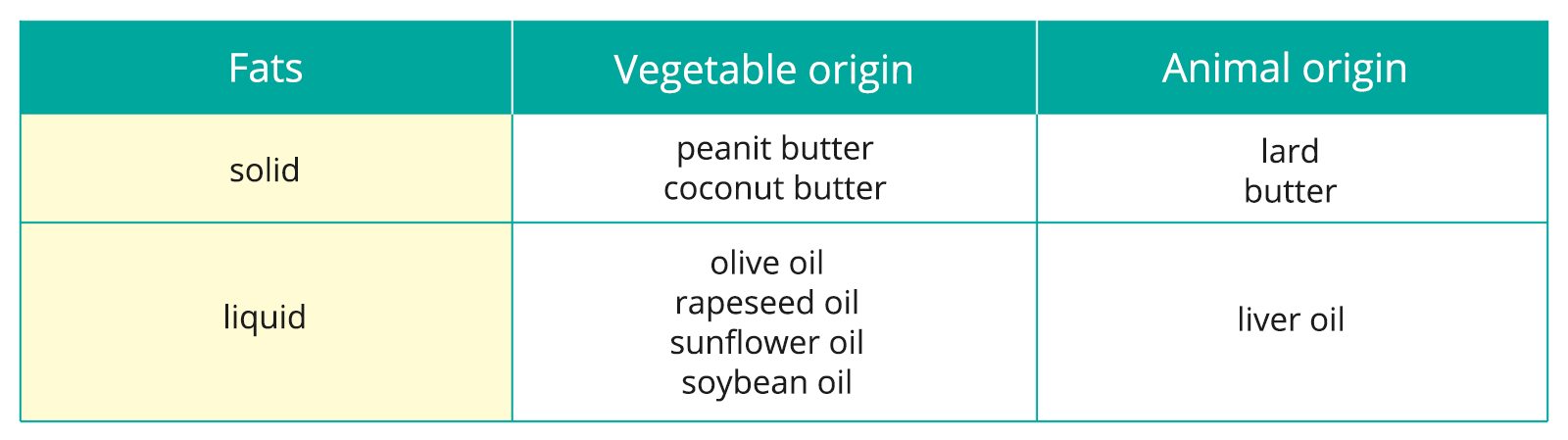
Analyse the information collected in the table. Answer the question: what is the relation between solid and liquid fats and animal and vegetable fats?
It can easily be seen that solid fats are mainly of animal origin and liquid - of vegetable origin. To learn what affects this dependence, let's conduct the experiment.
What is structure of vegetable and animal fats?
Solid animal fats are mainly saturated compounds, and vegetable fats – are unsaturated compounds.
butter,
lard,
sunflower oil,
rapeseed oil,
bromine water,
test tubes,
test tube holder,
burner
Put the butter in the first test tube, in the second one – lard, in the third – sunflower oil, and in the fourth – rapeseed oil.
Warm the test tubes with butter and lard so that these substances melt.
Add 3 cmIndeks górny 33 of bromine water to each tube and shake.
Types of fats
solid, olive oil, sunflower oil, rapeseed oil, soybean oil
| Fats | of plant origin | of animal origin |
|---|---|---|
| solid | ||
| olive oil, sunflower oil, rapeseed oil, soybean oil |
Complete the text.
Fats can be divided - due to state of ............ - into ............ and liquids and because of origin - into plant and animal.
What are the properties of the fats?
Before you watch the movie „Testing the properties of fats – dissolving oil in gasoline”, formulate a research question and hypothesis.
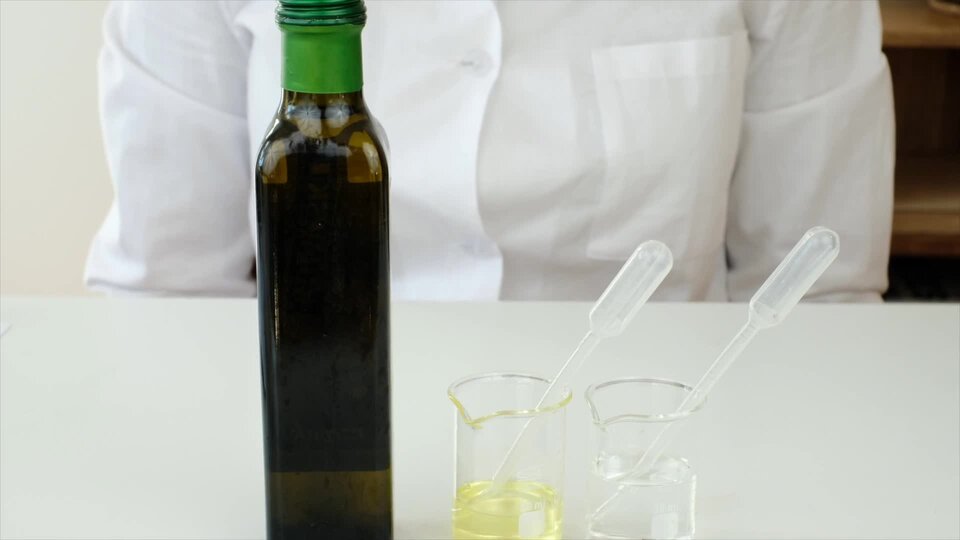

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Film przedstawia eksperyment: Testowanie właściwości tłuszczów - rozpuszczanie oleju w benzynie. Do przeprowadzenia eksperymentu potrzebne są: olej, benzyna, woda, pipeta, probówki. Przebieg: w jednej próbce należy zmieszać olej oraz benzynę. W drugiej nalezy zmieszać olej i wodę. W pierwszej probówce olej rozpuści się w benzynie. W drugiej probówce olej nie rozpuści się w wodzie.
Which substance will dissolve vegetable oil – water or gasoline?
Oil will dissolve in gasoline.
sunflower oil,
water,
gasoline,
test tubes.
Fill two test tubes with a few cmIndeks górny 33 of oil.
Add water to one of the tubes and shake.
Pour gasoline into the other and shake.
The fats do not dissolve in water, their structure is non‑polar. Fats dissolve well in organic solvents.
Look at the interactive illustration to find out why you cannot extinguish burning oil in a pan with water.
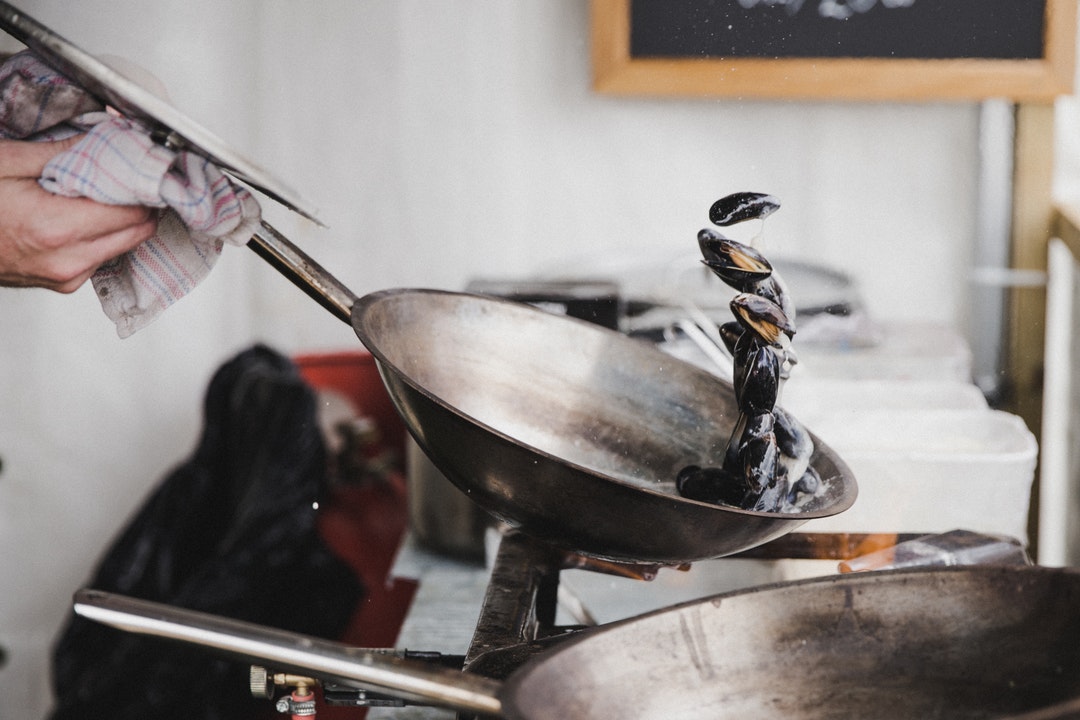

1. Water density is greater than the oil density, so after pouring into a container with burning oil it flows to the bottom.
2. Water poured into a frying pan with burning oil warms up to a temperature above 100°C
3. Water converst into gas that is why it spreads.
4. What should you do when the oil in the pan burns? Turn off the gas under the pan. Then with a calm motion cover the vessel so as to limit the supply of oxygen (oxygen sustains combustion).
Select correct answer.
- cod-liver oil is solid and animal oil
- cod-liver oil is liquid and plant oil
- cod-liver oil is liquid and animal oil
- cod-liver oil is solid and plant oil
Select the correct answer.
- some animal fats discolour the bromine water, because it is affected by the double bond between carbon atoms in fats molecules
- animal fats discolour the bromine water, because it is affected by a single bond between carbon atoms in fats molecules
- vegetable fats discolour the bromine water, because it is affected by the single bond between carbon atoms in fats molecules
- vegetable fats discolour the bromine water because it is affected by the double bond between carbon atoms in fats molecules
Summary
Fats are esters of glycerol and higher carboxylic acids.
Fats can be divided – due to the state of matter – into solid and liquid.
We divide the fats – due to the origin – into vegetable and animal.
Vegetable fats contain mainly unsaturated compounds, and animal fats – saturated compounds.
Vegetable fats (liquid) discolour the bromine water. It is affected by the presence of multiple bonds between carbon atoms in fats molecules.
Fats do not dissolve in water, but dissolve well in nonpolar solvents, e.g. in petrol.
Fats are necessary for the proper functioning of the body.
Keywords
fats, hydrolysis, saponification, mineral oil, vegetable oil, olive oil
Glossary
tłuszcze – estry glicerolu i wyższych kwasów karboksylowych
reakcja charakterystyczna – reakcja pozwalająca zidentyfikować daną substancję lub grupę związków