Ilustracja interaktywna
The interactive illustration below depicts commercial lettuce production, which is an example of hydroponic agriculture. Notice the intricacy of the process and consider its fantastic outcome: the green leafy lettuce seedlings. You can almost feel the warmth and humidity of the place, can’t you? Study the available information and apply your knowledge in the tasks below.
Na poniższej ilustracji przedstawiono przykład rolnictwa hydroponicznego - masową uprawę sałaty. Zwróć uwagę na proces uprawy i jego fantastyczne rezultaty – soczyste zielone sadzonki sałaty. Możesz niemal odczuć ciepło emanujące ze zdjęcia i poczuć wilgotne szklarniowe powietrze, prawda? Po zapoznaniu się z materiałem wykorzystaj zdobytą wiedzę do wykonania zadań.
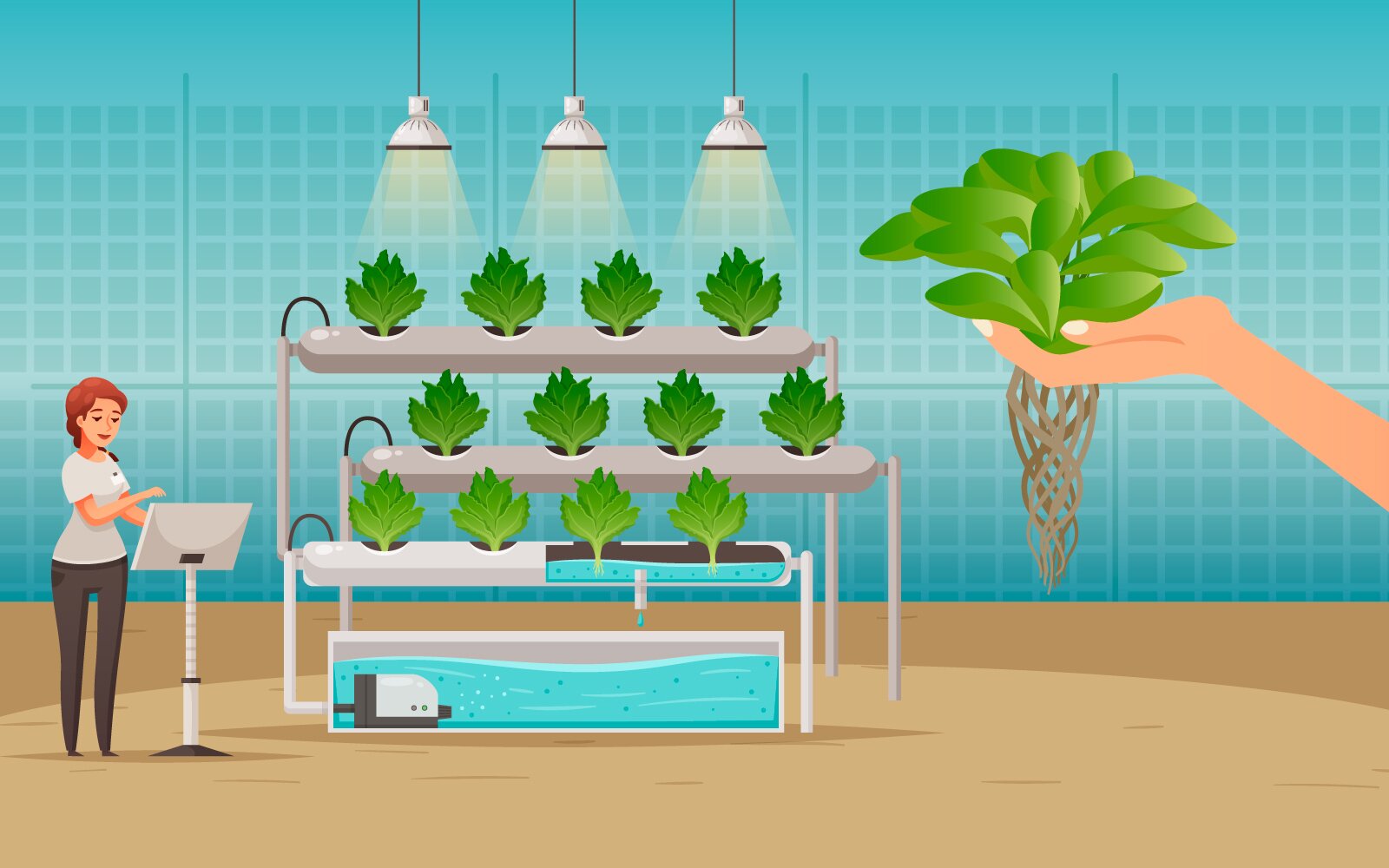

Pay attention to the sentences below and complete them with the correct words. Each word fits 2 sentences. There are 2 extra words which you do not need.
1 b. Before you 1. water, 2. plant, 3. water, 4. weed, 5. farm, 6. weed, 7. seed, 8. plant a new flower, ensure the pot’s size is appropriate.
2 a. Remember to 1. water, 2. plant, 3. water, 4. weed, 5. farm, 6. weed, 7. seed, 8. plant the pot depending on the flower’s needs.
2 b. Most flowers prefer to be provided with still 1. water, 2. plant, 3. water, 4. weed, 5. farm, 6. weed, 7. seed, 8. plant at room temperature.
3 a. When a gardener or farmer finds even one 1. water, 2. plant, 3. water, 4. weed, 5. farm, 6. weed, 7. seed, 8. plant it often means there will soon grow plenty of others.
3 b. A careful gardener never forgets to 1. water, 2. plant, 3. water, 4. weed, 5. farm, 6. weed, 7. seed, 8. plant his or her garden.
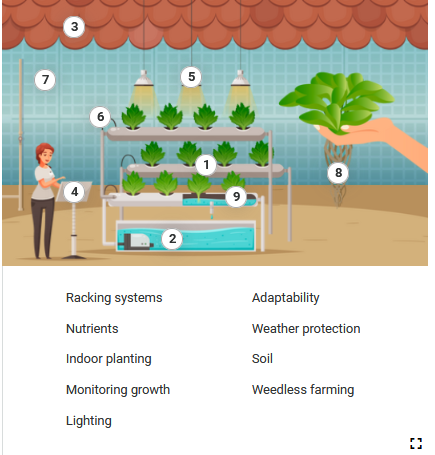
Study the illustration and do the tasks below. Click on the numbers and play the recordings to discover more information.
Zasób interaktywny dostępny pod adresem https://zpe.gov.pl/a/Dqn31nXd0
Ilustracja przedstawia wnętrze laboratorium, w którym znajdują się belki z roślinami ustawione jedna nad drugą. Nad górną belką ukazane są trzy lampy emitujące żółte światło. Pierwsza belka od dołu jest w połowie ukazana w przekroju, na którym zaprezentowano , że belki wypełnione są wodą. Pod ostatnią belką znajduje się szklane naczynie z wodą i urządzeniem w środku. Do naczynia przytwierdzone są rury odprowadzające wodę do belek. Po lewej stronie grafiki stoi kobieta przy pulpicie. Po prawej jest umiejscowiona ręka, która trzyma jedną roślinę w dłoni. Od góry ilustracji widoczne są dachówki. Ilustracja posiada dziewięć punktów interaktywnych, po naciśnięciu których pojawiają się nagrania. Transkrypcja do nagrań znajduje się poniżej.
RACKING SYSTEMS
Ilustracja nr 1 Roślina posadzona w otworze znajdującym się w półce.
NUTRIENTS
Ilustracja nr 2 Zbiornik na wodę znajdujący się pod półkami.
INDOOR PLANTING
Ilustracja nr 3 Dachówki znajdujące się na górze ilustracji.
MONITORING GROWTH
Ilustracja nr 4 Tablet umieszczony na statywie, na którym kobieta coś wpisuje.
LIGHTING
Ilustracja nr 5 Lampy zawieszone nad półkami z roślinami.
ADAPTABILITY
Ilustracja nr 6 Moduł składający się z kilku półek, na których w otworach posadzono rośliny.
WEATHER PROTECTION
Ilustracja nr 7 Ściana.
SOIL
Ilustracja nr 8 Sadzonka z korzeniami trzymana na dłoni.
WEEDLESS FARMING
Ilustracja nr 9 Przekrój półki, w której ukazano rozkład nawodnienia.
Study the sentences below and decide if they are true or false. Use the information from the interactive illustration.
- Study the sentences below and decide if they are true or false. Use the information from the interactive photograph.
- In Hydroponic farming, nutrients are constantly provided to plants. TRUEFALSE
- Hydroponic farmers often attend training and courses. TRUEFALSE
- The correct amount of fertilizer is carefully monitored and easily altered. TRUEFALSE
- In hydroponic agricultural models, air is always used to get nutrients to plants. TRUEFALSE
- The feeding and watering processes are supervised and tailored to plants’ needs. TRUEFALSE
- Typical elements of hydroponics are predictability and elimination of chemicals. TRUEFALSE
Drag the words below to the correct places. There are 2 extra words which you do not need.
- Hydroponics is characterised by 1. vertical, 2. urban, 3. seedlings, 4. predictability, 5. pesticides, 6. Herbicides, 7. avoidance, 8. disadvantageous because all the plants are continually monitored.
1. vertical, 2. urban, 3. seedlings, 4. predictability, 5. pesticides, 6. Herbicides, 7. avoidance, 8. disadvantageous are not used in a hydroponic agricultural model, because the plants seldom get illnesses.
- Due to the fact that the plants are grown from 1. vertical, 2. urban, 3. seedlings, 4. predictability, 5. pesticides, 6. Herbicides, 7. avoidance, 8. disadvantageous and they are planted, not sown into the ground, the use of soil is unnecessary.
- The plants also do not fall prey to vermin, and therefore 1. vertical, 2. urban, 3. seedlings, 4. predictability, 5. pesticides, 6. Herbicides, 7. avoidance, 8. disadvantageous are not used.
- Hydroponic agricultural models are resistant to changeable weather and 1. vertical, 2. urban, 3. seedlings, 4. predictability, 5. pesticides, 6. Herbicides, 7. avoidance, 8. disadvantageous temperatures.
- The possibility to grow plants even in cities or in 1. vertical, 2. urban, 3. seedlings, 4. predictability, 5. pesticides, 6. Herbicides, 7. avoidance, 8. disadvantageous areas, far away from villages, is hydroponics’ significant potential.
Fill in the gaps with the English translations of the words in brackets.
- In the hTu uzupełnij agricultural model the focus is placed on growing healthy plants.
- The farming takes place iTu uzupełnij and helps to increase productivity.
- Because there are no wTu uzupełnij there is no necessity to apply chemicals.
- The plants’ placement can be maximised by the use of a vTu uzupełnij racking system.
- Racks with plants can be easily rTu uzupełnij and their placement changed to make sure plants have perfect growing conditions.
- Easy changes and fTu uzupełnij are characteristic for hydroponics.