Points, lines and planes in space
Punkty, proste i płaszczyzny w przestrzeni
Learning objectives
You will learn to identify mutual position of lines in space, especially perpendicular lines that do not cross and also to apply the concept of an angle between the line and the plane as well as the dihedral angle between half‑planes.
Learning effect
You identify mutual position of lines in space, especially perpendicular lines that do not cross and also apply the concept of an angle between the line and the plane as well as the dihedral angle between half‑planes.
Prepare information about the following subjects:
Mutual position of the line and the planeplane.
Mutual position of lines in space.
The angle between the line and the planeplane.
The dihedral angledihedral angle between half‑planes.
Check if information you prepared is the same as the following one:
1. Mutual position of the line and the planeplane
a line is located on the plane (each point of the line is also a point of the planeplane),
a line breaks the planeplane (the line has exactly one common point with the planeplane),
a line is parallel to the planeplane and has no common points with it.
2. Mutual position of lines in space
Lines overlap (they are parallel),
Lines are located on one planeplane and cross at one point,
Lines are located on one planeplane and have no common points (they are parallel),
Lines are not located on one planeplane and have no common points (they are oblique).
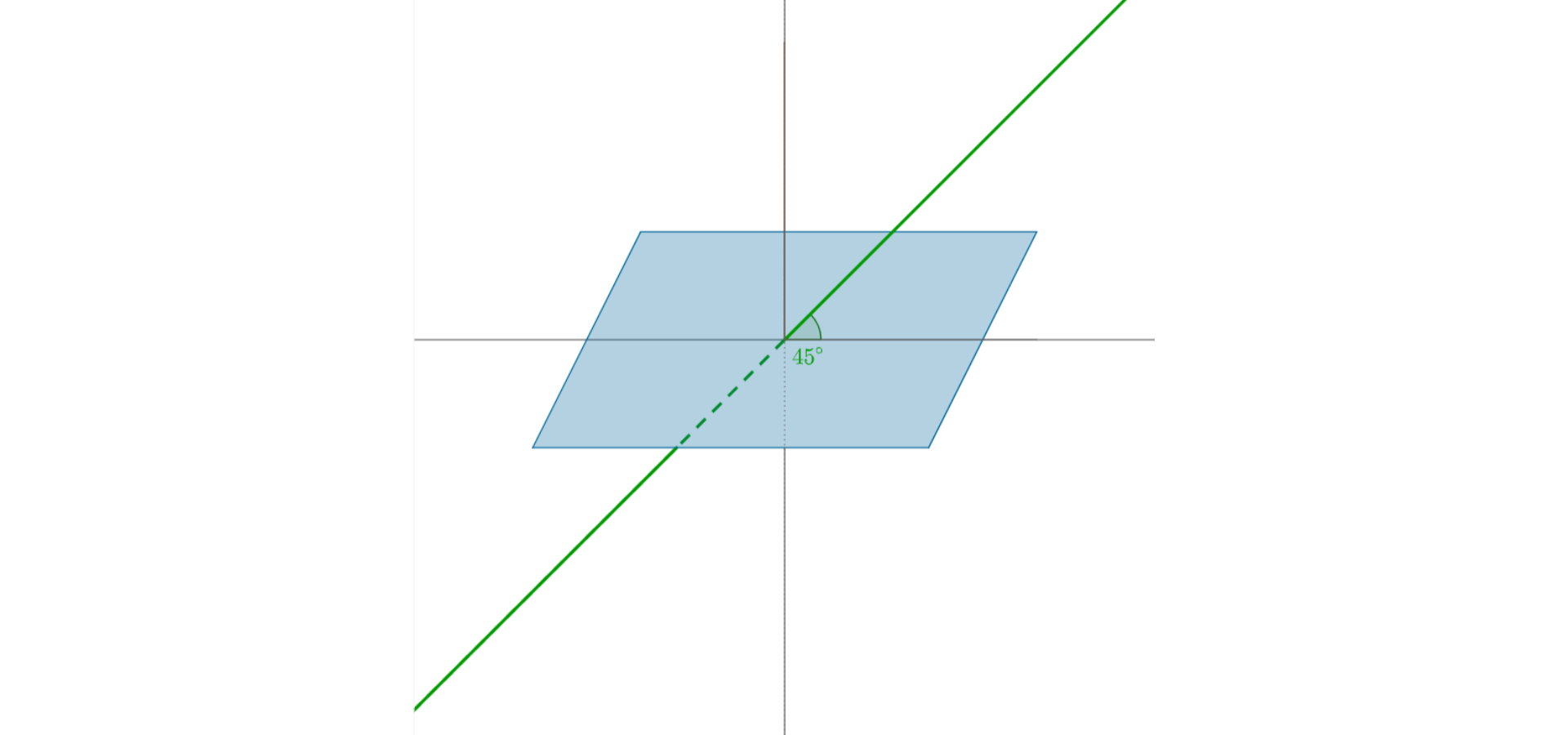
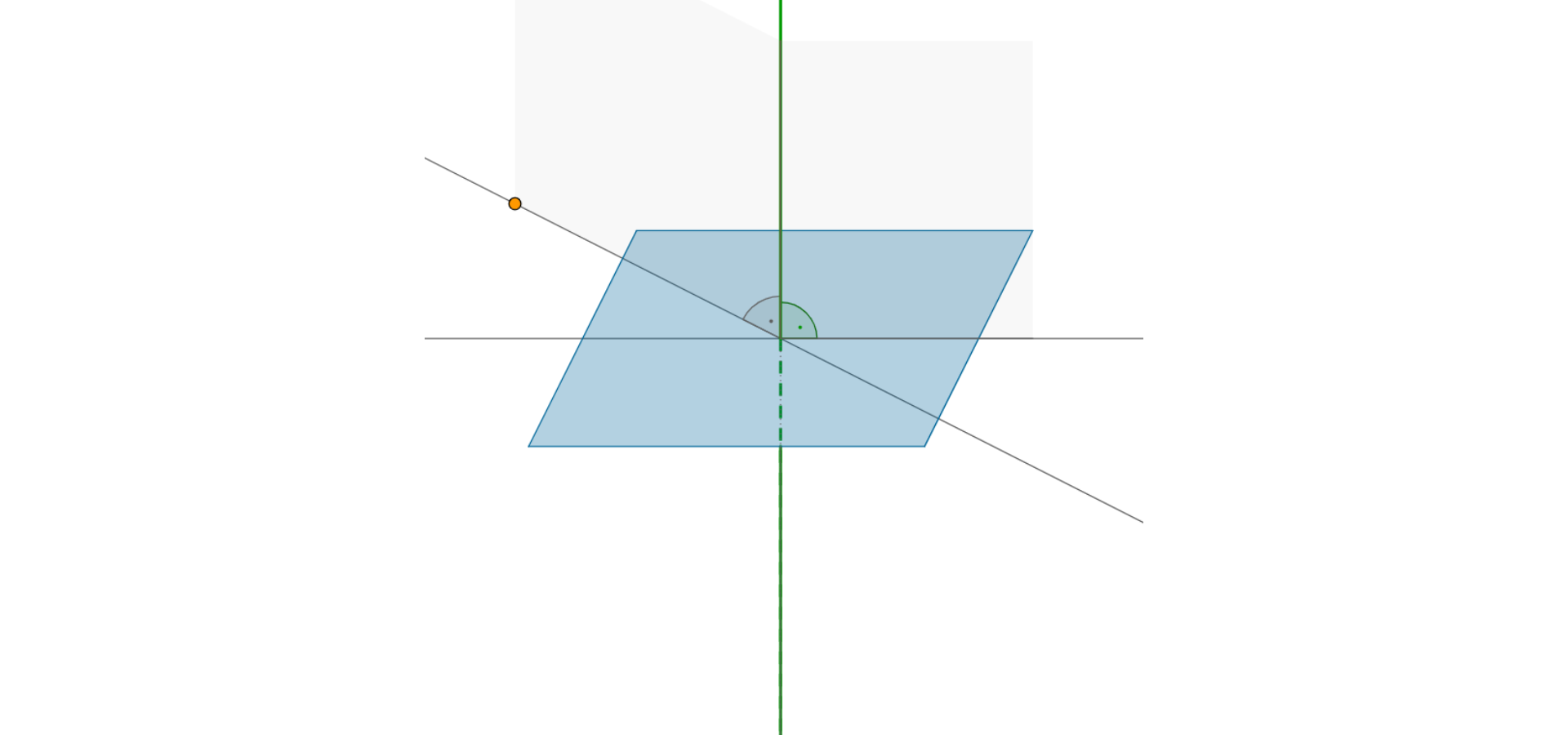
3. The angle between the line and the planeplane
The line k and the planeplane p are perpendicular only and only if the line k is parallel to each line located on the planeplane p,
The angle between the line k and the plane pangle between the line k and the plane p is the acute angle between this line and orthographic projection on the planeorthographic projection on the plane p,
If the line l breaks the planeplane p and is not perpendicular to it, the line k is an orthographic projection of the line l on the planeplane p, the line m is located on the planeplane p and crosses the line l, then the line m is perpendicular to the line l only and only if it is perpendicular to the line k (theorem about three perpendicular linesperpendicular lines).
4. The dihedral angledihedral angle between half‑planes
the dihedral angledihedral angle is the sum of two half‑planes with common edge and one of two areas that this half‑planes cut from the space,
the linear anglelinear angle of the dihedral angledihedral angle is the common part of the dihedral angledihedral angle and the planeplane perpendicular to its edge.
Open the applet and observe the angle that a line creates with a planeplane. Compare animations with information you prepared.
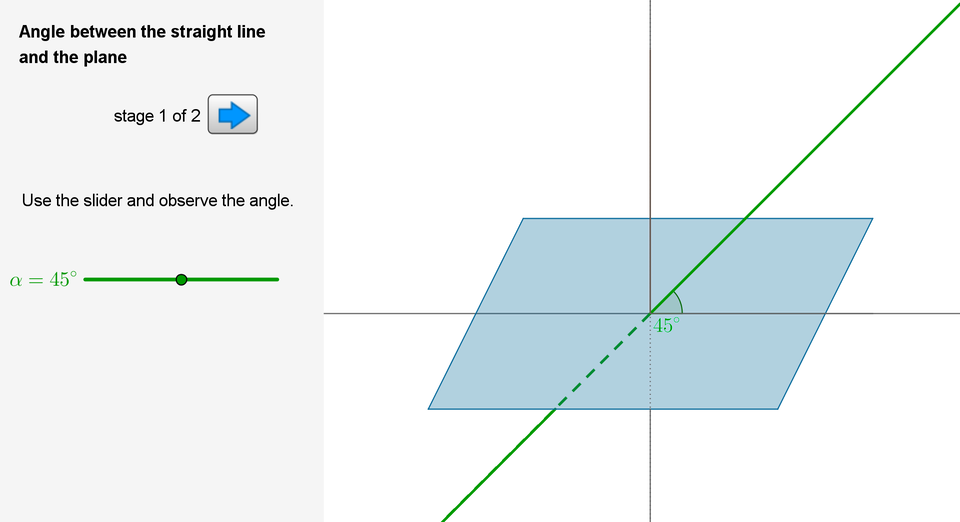
Zasób interaktywny dostępny pod adresem https://zpe.gov.pl/a/Dt3WttEZ6
There are lines a, b and c. How can lines a and b be located in relation to each other if lines a, b and c are not located on the same planeplane and the line b has one common points with the line a and one common point with the line c. Make a proper drawing.
There are three noncollinear points A, B, C on the planeplane p. The distance from the point A and the line BC and the distance between points A and B are the same and are equal to 4 cm. The length of the distance AC is equal to 5 cm. The line segment AS is perpendicular to the planeplane p and its distance is 12 cm. Calculate the area of the triangle BCS. Make a proper drawing.
Calculate the dihedral angledihedral angle knowing that the distance between the point P located on the wall of this angle and its edge is equal to 15 cm. The distance from the point P and the other wall of this angle is equal to 7,5 cm. Make a proper drawing.
An extra task:
There is a square KLMN. Prove that triangles KLS and LMS are right‑angled if we know that the line segments NS is perpendicular to the planeplane KLMN.
Do the revision exercises.
Remember:
A line can be located on the planeplane, break the planeplane or have no common points with the planeplane.
Two lines in space can overlap, be located on one planeplane or not be located on one planeplane and have no common points (be oblique).
The line k and the planeplane p are perpendicular only and only if the line k is parallel to each line located on the planeplane p.
The angle between the line k and the plane pangle between the line k and the plane p is the acute angle between this line and orthographic projection on the planeorthographic projection on the plane p.
If the line l breaks the planeplane p and is not perpendicular to it, the line k is an orthographic projection of the line l on the planeplane p, the line m is located on the planeplane p and crosses the line l, then the line m is perpendicular to the line l only and only if it is perpendicular to the line k (theorem about three perpendicular linesperpendicular lines).
The dihedral angledihedral angle is the sum of two half‑planes with common edge and one of two areas that this half‑planes cut from the space.
The linear anglelinear angle of the dihedral angledihedral angle is the common part of the dihedral angledihedral angle and the planeplane perpendicular to its edge.
Exercises
In the cuboid ABCDEFGH the line perpendicular to the plane BCGF is:
- the line AE
- the line AG
- the line AB
- the line BH
Draw a right triangular prism ABCA’B’C’. Mark the angle at which the diagonal BA’ of the lateral face ABB’A’ is inclined to the lateral face BCC’B’.
Draw any dihedral angle. Mark the linear angle of this dihedral angle. Write all its elements in English.
Indicate which pairs of expressions or words are translated correctly.
- kąt nachylenia prostej k do płaszczyzny p - angle between the line k and the plane p
- kąt dwuścienny - dihedral angle
- półpłaszczyzna - half-plane
- kąt liniowy - linear angle
- proste równoległe - perpendicular lines
- proste skośne - parallel lines
- kąt dwuścienny
- proste skośne
- rzut prostokątny na płaszczyznę
- prosta przebijająca płaszczyznę
- oblique lines
- the line that breaks the plane
- the dihedral angle
- the orthographic projection on the plane
- kąt nachylenia prostej k do płaszczyzny p
- the angle between the line k and the plane p
Glossary
kąt nachylenia prostej k do płaszczyzny p
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: angle between the line k and the plane p
kąt dwuścienny
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: dihedral angle
półpłaszczyzna
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: half‑plane
prosta przebijająca płaszczyznę
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: line that breaks the plane
kąt liniowy
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: linear angle
proste skośne
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: oblique lines
rzut prostokątny na płaszczyznę
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: orthographic projection on the plane
proste równoległe
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: parallel lines
proste prostopadłe
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: perpendicular lines
płaszczyzna
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: plane
Keywords
angle between the line k and the plane pangle between the line k and the plane p - kąt ostry między tą prostą i jej rzutem prostokątnym l na płaszczyznę p
dihedral angledihedral angle - suma dwóch półpłaszczyzn o wspólnej krawędzi i jednego z dwóch obszarów, które te półpłaszczyzny wycinają z przestrzeni
line that breaks the planeline that breaks the plane
oblique linesoblique lines
orthographic projection on the planeorthographic projection on the plane