Ilustracja interaktywna
All right, so you read the lecture and did the tasks, but how well do you remember it? Did you understand it well enough to label the organs in the picture? Let’s try that!
No dobrze, przeczytałeś/przeczytałaś wykład i zrobiłeś/zrobiłaś zadania, ale czy pamiętasz informacje w nich zawarte? Czy zrozumiałeś/zrozumiałaś wszystko na tyle dobrze, żeby móc zidentyfikować poszczególne organy na ilustracji? Sprawdźmy!

Complete the crossword. What’s the hidden word?
Zasób interaktywny dostępny pod adresem https://zpe.gov.pl/a/DvKB8WmEC
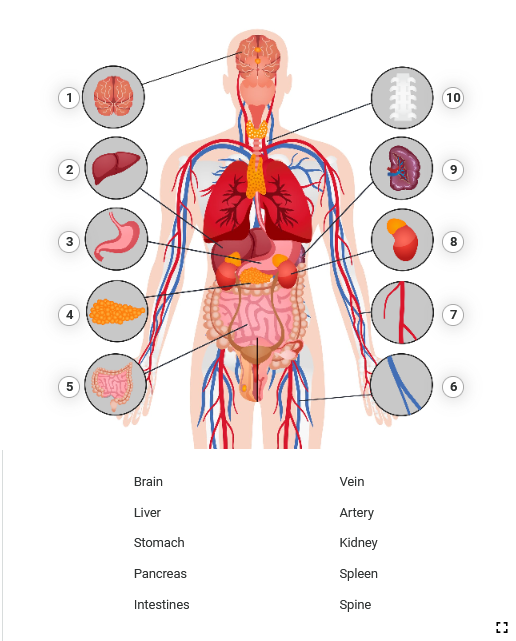
Grafika przedstawia zarys sylwetki człowieka, od głowy do połowy ud, z widocznymi układami krążenia, oddechowym oraz pokarmowym. Grafika posiada dziesięć punktów interaktywnych, po naciśnięciu których pojawia się tekst oraz nagranie. Transkrypcja do nagrań znajduje się poniżej.
Brain
The brain is the control centre of the human body. It forms the core of the central nervous system by creating, sending and processing nerve impulses, thoughts, emotions, physical sensations, and more. The brain is inside the skull, which protects it from injury.
Grafika nr 1 przedstawia mózg.
Liver
The liver is one of the most important organs in our body. It helps convert nutriens into usable substances, detoxifies certain substances and filters blood coming from the digestive tract.
Grafika nr 2 przedstawia wątrobę.
Stomach
Your stomach is an organ that digests food. It is part of your digestive tract. When food gets into the stomach, the organ contracts and produces acids and enzymes that break down food.
Grafika nr 3 przedstawia żołądek.
Pancreas
The pancreas plays an essential role in converting the food we eat into fuel for the cells. the pancreas has two main finctions: it helps in digestion and it regulates blood suger.
Grafika nr 4 przedstawia trzustkę.
Intestines
The intestines are responsible for breaking food down, absorbing nutriens from it and solidifying the waste. The small intestine is almost 7 metres long and it is the longest part of the digestive tract. This is where most of your digestion takes place.
Grafika nr 5 przedstawia jelita.
Vein
A vein is a blood vessel that transports deoxygenated blood to the right side of the heart.
Grafika nr 6 przedstawia żyłę.
Artery
An artery is a blood vessel that carries oxygen‑rich blood away from your heart to other parts of your body. The main artery is called the aorta.
Grafika nr 7 przedstawia tętnicę.
Kidney
The kidney helps filter blood and remove waste from the body. Each kidney contains about a million tiny units for filtration. It is possible to live with just one kidney. If a kidney fails, dialysis can filter the blood until the person can get a kidney transplant or their kidney recovers some function.
Grafika nr 8 przedstawia nerkę.
Spleen
The spleen has several important functions: it fights invading germs in the blood as it contains infection‑fighting white cells, it controls the level of blood cells, it filters the blood and removes any old or damaged red blood cells.
Grafika nr 9 przedstawia śledzionę.
Spine
The spine, or backbone, is the central support structure of the body. It connects different muscles and bones. Your spine helps you move: sit, stand, walk, twist and bend. The backbone may be damaged by some back injuries and other problems, which can cause back pain.
Grafika nr 10 przedstawia fragment kręgosłupa szyjnego.
Type the English names of the organs next to their Polish translations.
- The kidneysaortaveins filter out waste products from the blood.
- You should stay straight, so that your limbsspinepancreas won’t deform.
- PancreasBrainHeart helps us digest food and produces insulin.
- Excessive alcohol consumption may destroy your limbsspineliver.
- The intestinesaortaskidneys are long, tube-like parts of our body through which digested food travels.
- Veins transport oxygenateddeoxygenatedfiltered blood to the heart.
- The aorta is an example of a/an arteryveinlimb.
- The spleen helps us fight germsacidsenzymes.