Obtaining salts in reactions of acids with metals
that salts are ionic compounds composed of cations of metals and anions of an acid radical.
to write chemical equations for reactions of certain metals with acids that lead to the creation of salt;
to predict, based on the activity series of metals, which metals displace hydrogen from acids as well as to indicate those which do not have such properties.
Some metals, such as zinc, magnesium, aluminium and iron, react with hydrochloric acid. These reactions produce corresponding salts and give off hydrogen. We say that these metals displace hydrogen from acid. There are metals, such as copper, which do not react with hydrochloric acid.
Reactions of metals with a diluted solution of sulfuric acid
Do selected metals react with a diluted solution of sulfuric acid?
Select one of the presented hypotheses and then verify it.
Only some metals react with a diluted solution of sulfuric acid.
All metals react with a diluted solution of sulfuric acid.
test tubes,
diluted solution of sulfuric acid,
metals: magnesium, iron, copper, zinc,
abrasive paper,
wooden skewer,
matches.
Take four test tubes and pour 2–3 cmIndeks górny 33 of the diluted sulfuric acid solution into each.
To each of them, add a different piece of metal that has been cleaned with abrasive paper: magnesium ribbon, iron wire, zinc plate, copper wire.
Observe the changes that occur.
Bring the burning wooden skewer close to the outlet of each test tube.
Magnesium, zinc and iron react with a diluted solution of sulfuric acid. These reactions produce salt and hydrogen:
Copper does not react with a diluted sulfuric acid solution:
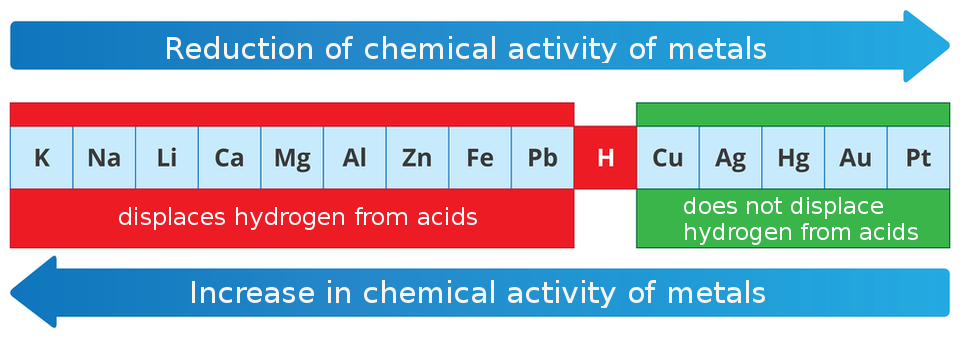
Activity series of metals
Chemists have ordered metals according to their changing chemical activity. This order is called the activity series of metals. There are usually two ways of presenting metals in this collection: by their decreasing or increasing chemical activity. Hydrogen, which has been listed in this series, separates metals into those that displace it from acids and those that do not have such property.
The following example shows metals ordered by their decreasing chemical activity.

Based on the activity series of metals, we can conclude that, for example, sodium displaces hydrogen from acid (salt and hydrogen are created). The reaction of this metal with hydrochloric acid is described in the following equation:
On the basis of the activity series, we can predict that copper, mercury, silver, gold and platinum will not displace hydrogen from acids. However, we cannot assess whether they will or will not react with nitric acid or sulfuric acid to produce products other than hydrogen.
Before watching the movie „Experiment: Hydrochloric acid + Magnesium”, think about the reaction you will observe. Formulate a research question and hypotheses. You can make a note on the form.

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Film pokazuje eksperyment – reakcję kwasu chlorowodorowego, hydrochloric acid oraz magnezu, magnesium. Będziesz potrzebować: kwas chlorowodorowy, wstążkę magnezową, zapalniczkę, pipetę, łuczywo, korek. Do probówki dodajemy pipetą kilka kropli kwasu chlorowodorowego i kawałek wstążki magnezowej. Zachodzi burzliwa reakcja, wydziela się gaz. Zatykamy lekko probówkę korkiem. Zapalamy łuczywo. Otwieramy korek i przykładamy zapalone łuczywo do wylotu probówki – wydobywający się z probówki gaz spala się wybuchowo.
Assign the symbols of metals to corresponding groups.
Ca, Mg, Pb, Au, Al, Zn, Ag, Hg, Li, Pt, K, Na, Fe, Cu
| Metals which displace hydrogen from acids | |
|---|---|
| Metals which do not displace hydrogen from acids |
Create a multiple-choice test based on today's lesson. Then exchange your questions with a friend or classmate.
Question: ...
- ...
- ...
- ...
- ...
Conclusion
Some metals react with acids with hydrogen evolution. The second product of this reaction is salt.
Copper does not displace hydrogen from acids.
Based on the activity series of metals, we can assess whether a metal displaces hydrogen from acids.
Keywords
acid, metal, chemical equation, salt, obtainment of salt, reaction of acid with metal
Glossary
szereg aktywności metali – metale ułożone według zmieniającej się stopniowo (malejącej lub rosnącej) aktywności chemicznej