The wealth of nature
conservation of biological diversity is in the common interest of all the people;
international cooperation has significant importance in conservation of biological diversity;
sustainable development is supposed to ensure proper standard of life for modern societes and make it possible for the future generations to use the natural resources.
to characterize levels of biological diversity;
to provide examples of threats to biodiversity;
to describe methods of nature conservation.
Levels of biodiversity
Earth's biodiversity is the effect of existence of large amounts of spieces consisting of diverse individuals, which live in various terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. Genetic diversity within spieces or population depends on the number of different alleles of the given gene. Species diversitySpecies diversity, in turn, results from historical factors – evolutionary and modern changes – existence of climate zones, diverisfied terrains, as well as the relations between living elements of ecosystems. Currently, the biodiversity is mainly affected by the human activity.
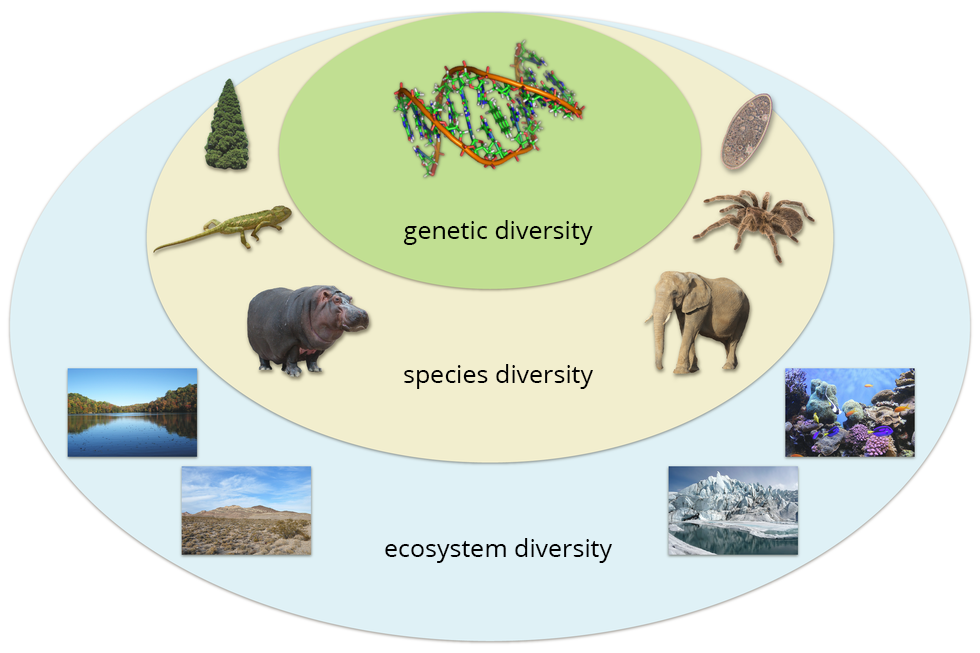
Explain what species diversity is and describe factors that determine it.
Threats to biodiversity and extinction of species
In the history of the Earth several times there was a phenomenon of natural extinction of species, caused by climate changes or sudden volcanic eruptions and asteroid impacts. The extinction of species is an ongoing process which started around 10,000 years ago. The main factor causing it is human activity.

Conservation of nature
The existence of each species, including the human species, depends on the preservation of its genetic diversity. The aim of the nature conservation is to preserve natural ecological and evolutionary processes, to preserve diversity of organisms as well as optimal conditions for their life, to rationally use natural resources and to preserve the beauty of the landscape. Nature conservation activities are aimed at recreating or multiplying natural elements destroyed or changed by human activity.

Nature conservation requires high levels of financial resources from the national and local governments. Do you think it is worth spending so much on the conservation of nature? Justify your opinion.
Move each of the following items to the appropriate group.
diversification of natural habitats, diversification of ecosystems within one biome, emergence of new species from isolated populations, climate diversity of biomes, diversification of phenotypic features in a population, existence of a few alleles of the same genes, the high level of heterozygosity in a population, existence of many species in given ecosystem
| genetic diversity | |
|---|---|
| species diversity | |
| ecosystem diversity |
Select in the list below all the activities which purpose is protection of nature.
- maintaining natural ecological and evolutionary processes
- genetic modification of organisms which increases their resistance to unfavorable conditions
- preservation of diversity of organisms and optimal living conditions
- rational use of natural resources and preservation of the beauty of the landscape
- reconstruction or multiplication of elements of nature which were destroyed or changed by human activity
- creation of artificial ecosystems strictly controlled by human
Match the form of nature protection to activities undertaken within its framework.
undertaking necessary activities improving the status of protected ecosystems or communities, transfer of the endangered place of nature to a safe post that ensures appropriate living conditions., complete cessation of all human activities in the ecosystem or community, activities to preserve the natural component in its natural occurrence
| passive protection | |
| active protection | |
| in situ protection | |
| ex situ protection |
Keywords
species diversity, in situ protection, ex situ protection
Glossary
ochrona bierna – ochrona ścisła w odniesieniu do ekosystemów; zupełne i stałe zaniechanie jakiejkolwiek działalności człowieka, mające na celu zachowanie naturalnego przebiegu procesów przyrodniczych
ochrona czynna – ochrona częściowa w odniesieniu do ekosystemów, dopuszczanie ingerencji człowieka w przyrodę obszaru chronionego w celu zachowania chronionego ekosystemu lub jego wybranych składników w optymalnym stanie albo przywrócenia go do stanu pożądanego
ochrona ex situ – ochrona dziko żyjących gatunków roślin, zwierząt i grzybów poza miejscem ich naturalnego występowania, polegająca na przeniesieniu zagrożonych organizmów na miejsce, w którym można zapewnić im trwałe i bezpieczne bytowanie oraz warunki umożliwiające zwiększenie liczebności
ochrona in situ – ochrona dziko żyjących gatunków roślin, zwierząt i grzybów w miejscu ich naturalnego występowania poprzez działania mające na celu zachowanie ich siedlisk i umożliwienie zwiększenia liczebności
różnorodność gatunkowa – jeden z poziomów różnorodności biologicznej; liczba gatunków w danym ekosystemie lub na danym obszarze