World War II - a revision lesson
to list the most important events of 1939‑1945;
to describe the most important facts, names and dates;
to characterize the consequences of the World War II;
to explain how did the war influence the events in the world.
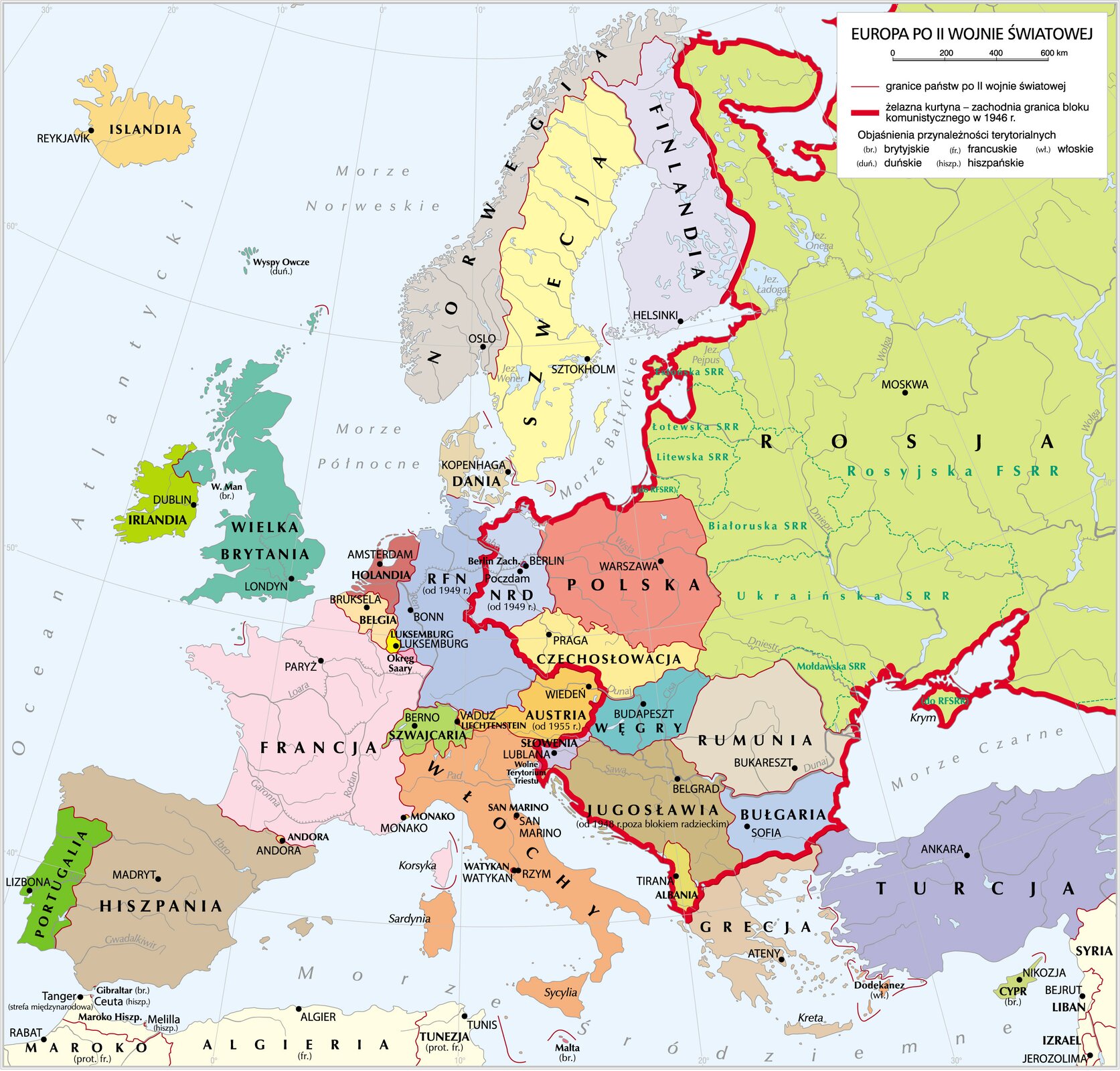
Nearly 20 years after the Great War, peace in Europe was threatened again. Growing power of the Third Reich and its political and military activity, including The Anschluss of Austria and the invasion in Czechoslovakia caused the world to face war once again. World War II began on 1st of September 1939, when German army attacked Poland. On 17th September 1939, in accordance with the Ribbentrop‑Molotov pact, the USSR army joined the German army attacking Poland from the East. Until 1941, under German occupation and the occupation of their allies was nearly entire continental Europe. The USSR also had its armaments policy and expanded its territory by fighting against Finland and by invading the Baltic countries. A turning point of the conflict was the attack of Germany on the USSR, on 22nd of June 1941, which not only decided on changes in the alliances (the Soviets joined the Allies), but also forced the Third Reich to fight on two fronts. On the conquered and occupiedoccupied territories, the Germans introduced the policy of terror and persecution, especially among the Jews and the Gypsies, persecuting and exterminating the enemies, e.g. in concentration camps. In 1941, the United States of America joined the war, as a result of the attack on their naval base in Pearl Harbor conducted by the Japanese air force. This extended the territory of military action nearly to the entire world. The anti‑Hitler coalition, which main force was the Big Three – the rulers of the USA - Roosevelt, the USSR – Stalin and of Great Britain – Churchill, played a vital role in military and political plans during the war, and also after it finished, while establishing the new order. The victories and the might of the German army was broken in the battles of Stalingrad and Kursk in 1943. Since then, the Allied forces started the offensive, forcing the German soldiers to retreat, and leading to the ultimate defeat in May of 1945. It was not the end of World War II. It lasted until 2nd of September 1945 – the capitulation of Japan, which was caused by the use of new type of weapons of mass destruction – the atomic bomb. The conflict of 1939‑1945 was the biggest war in the history of the world and took place in Europe, North Africa, Far East and all the oceans.
The armed conflict of 1939‑1945, called the World War II, was the most bloody of all the conflicts in the history of the world until this day. Within 6 years over 60 million people died all over the world, which was around 3% of the population of that time. The total number of military victims was nearly 25 million of fallen soldiers, the rest were civilians. In addition, it is assumed that another 20 million were the victims of hunger and diseases connected with war and its direct causes. The biggest loss among European populations was suffered by the people of Jewish origin. Nearly 78% of them was killed as a result of the HolocaustHolocaust policy.
Match the facts to the correct group.
11.11.1918, Kursk salient, Verdun, 08.05.1945, Józef Piłsudski, Tsar Nicholas II, The Assassination in Sarajevo, Triple Entente, October Revolution, Treaty of Versailles, Hiroshima, D-Day, Triple Alliance, Battle of England, Big Three, Warsaw Uprising
| World War I | |
|---|---|
| World War II |
Keywords
Totalitarian regime, Holocaust, deportation, occupation, overloading, independence
Glossary
Totalitaryzm – system rządów politycznych połączony z uzasadniającą jego istnienie ideologią, która głosi całkowite podporządkowanie jednostki i pełną kontrolę przez państwo społeczeństwa.
Ruch oporu – oddziały, których celem jest walka z okupantem kraju najczęściej sposobami partyzanckimi. Swoją działalność rozpoczynają najczęściej po zaprzestaniu regularnych działań wojennych.
Konspiracja – tajna działalność prowadzona przez organizacje polityczne skierowana przeciw władzy, najczęściej okupanta kraju. Ma bezpośredni związek z działaniami ruchu oporu.
Holokaust – prześladowanie i zagłada ok. 6 mln Żydów, dokonana w czasie II wojny światowej przez III Rzeszę i wspierana przez jej sojuszników.
Deportacja – przymusowe przesiedlenie (wywózka), najczęściej do odległego miejsca, połączone z ograniczeniem wolności.
Okupacja – czasowe zajęcie jakiegoś terenu (np. państwa) przez wrogie siły i wprowadzenie tam swojej władzy.
Dyplomacja – wszelkie czynności jakie prowadzi państwo w celu rozwiązania w pokojowy sposób problemów międzypaństwowych.
Prześladowania – celowe nękanie, szykanowanie i wyrządzanie krzywdy wybranym osobom lub grupie osób, którego celem jest ich upokorzenie lub wyniszczenie.
Niepodległość – niezależność państwa od wpływu innych państw, instytucji na swoje działania.